New criteria help identify more patients in early stages of disease, promote better care and stimulate research to slow and prevent COPD.
TOP INSIGHT
Smokers who met two of the three additional criteria were designated as having Probable COPD. They had an 88 percent greater chance of losing significant lung function and an 89 percent greater chance of dying.
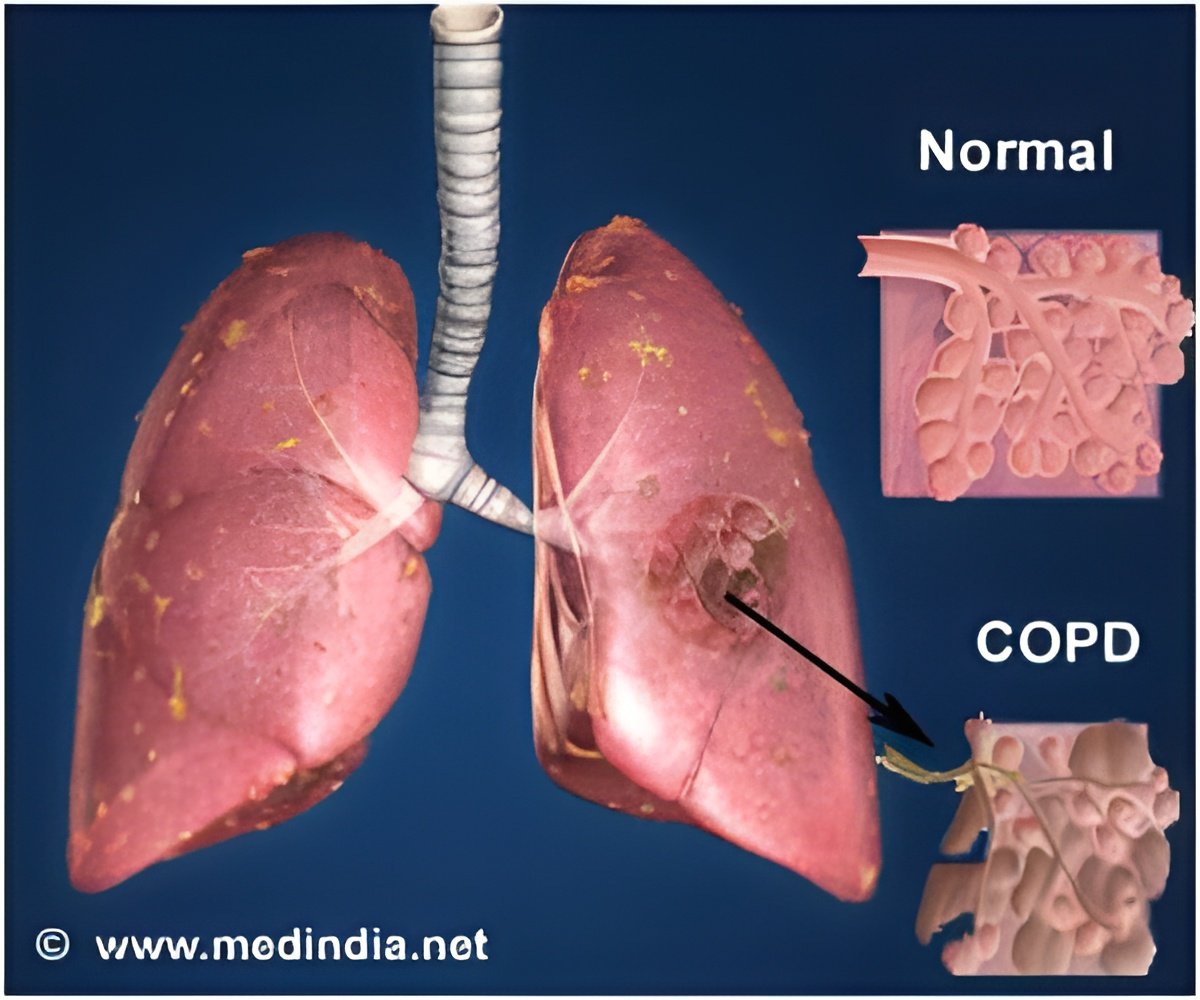
The researchers evaluated 8,784 smokers and former smokers enrolled in the COPDGene® study. At enrollment, the researchers documented patients' environmental exposures (smoking), symptoms (shortness of breath, chronic cough and phlegm), structural abnormalities on CT scans (emphysema, gas-trapping and airway wall thickness) and lung function or spirometry (total volume of air exhaled from the lungs, and the volume of air exhaled in one second). They then correlated those measures with mortality and loss of lung function five years later and compared them with smokers with none of the other criteria.
All patients met one of the criteria: smoking history. Those meeting either one, two or three additional criteria all had increased risks of losing significant lung function in five years or dying.
Smokers meeting one of the other three criteria were designated as having Possible COPD. Their risk of losing significant lung function was 26 percent greater than smokers meeting no additional criteria, and a 28 percent higher chance of dying within five years.
Those with all four diagnostic criteria were designated as having Definite COPD. They had a 188 percent greater chance of losing significant lung function over five years and more than 5 times the risk of dying.
"Right now people who do not meet the current diagnostic criteria for COPD are not included in clinical trials of experimental COPD therapies. Our proposed diagnostic criteria could open clinical trials to these people, stimulate important research of potential therapies to slow, stop or even prevent progression of the disease."
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email