Recent findings could improve early detection of osteoarthritis, the most common joint disorder, affecting about one-third of older adults and for which currently there is no cure.
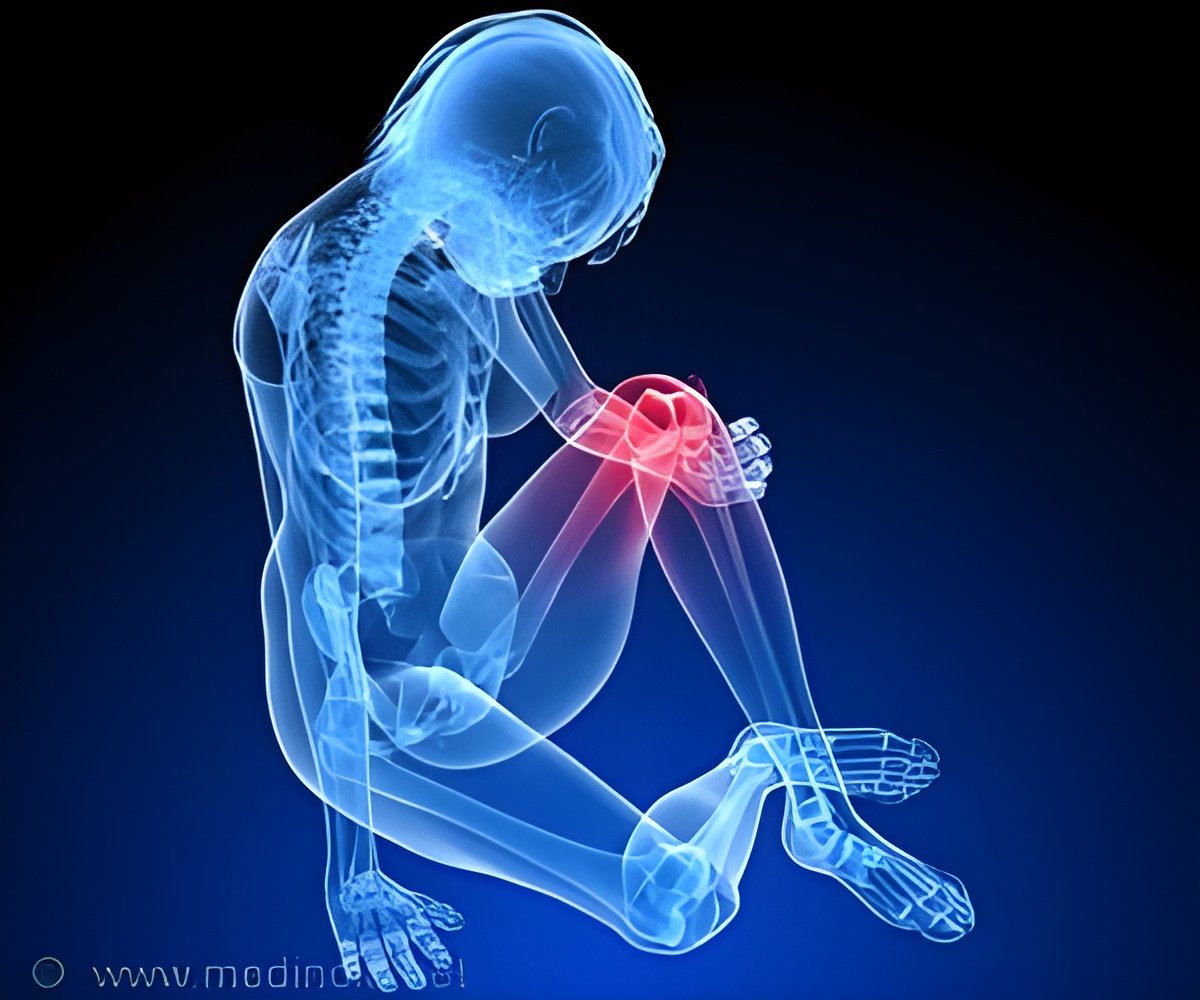
Osteoarthritis is a painful condition marked by the deterioration of cartilage—firm, rubbery tissue that cushions bones and prevents them from rubbing together. At the earliest stages of the disease, cartilage loses molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), which reduces the ability of the tissue to resist impact caused by physical activity. But until now, little was known about how GAG loss affects the functioning of cartilage across a wide spectrum of activities, from walking to running and jumping.
To address this question, Grodzinsky and his team developed a new system to measure the biomechanical properties of cartilage in response to cyclic compression forces that simulated a range of physical activities, each occurring at a different timescale. GAG-depleted cartilage was less capable of increasing its stiffness to deal with forces associated with high-rate activities such as running, when compared with normal tissue. Moreover, GAG loss resulted in a dramatic increase in the ability of fluids to flow out of cartilage, which is expected to diminish protection against impact caused by fast activities.
Together, the findings show how GAG depletion at the earliest disease stages could affect the nanoscale properties of cartilage, reducing the ability of this tissue to withstand high-rate activities. "We discovered that GAG-depleted tissue is most vulnerable to high rates of loading and not just the magnitude of the load," Grodzinsky says. "This finding suggests that people with early degradation of cartilage, even before such changes would be felt as pain, should be careful of dynamic activities such as running or jumping."
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email