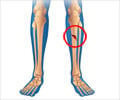
Lean elders with lower BMI are at higher risk of hip fracture. Intake of carotenoids could reduce the fracture risk among them.
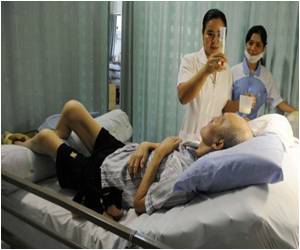
Also, in men, hip fracture risk decreased with increasing intakes of total vegetables and of total carotenoids, particularly β-carotene. The protective effect was higher in lean men than in men with higher BMI. In contrast, the intake of vegetables or carotenoids had no association with hip fracture risk in women, regardless of levels of BMI.
Cartenoids, which are found many fruits and vegetables (and especially in yellow and orange pigmented vegetables) are converted to vitamin A in the body. The researchers conclude that clinical trials are needed to demonstrate the efficacy of carotenoid supplementation on reduction of hip fracture risk in elderly men. The findings may have important public health implications on hip fracture prevention, particularly among Asians.
Abstracts from the IOF Regionals 3rd Asia-Pacific Osteoporosis Meeting have been published in the scientific journal Osteoporosis International.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email