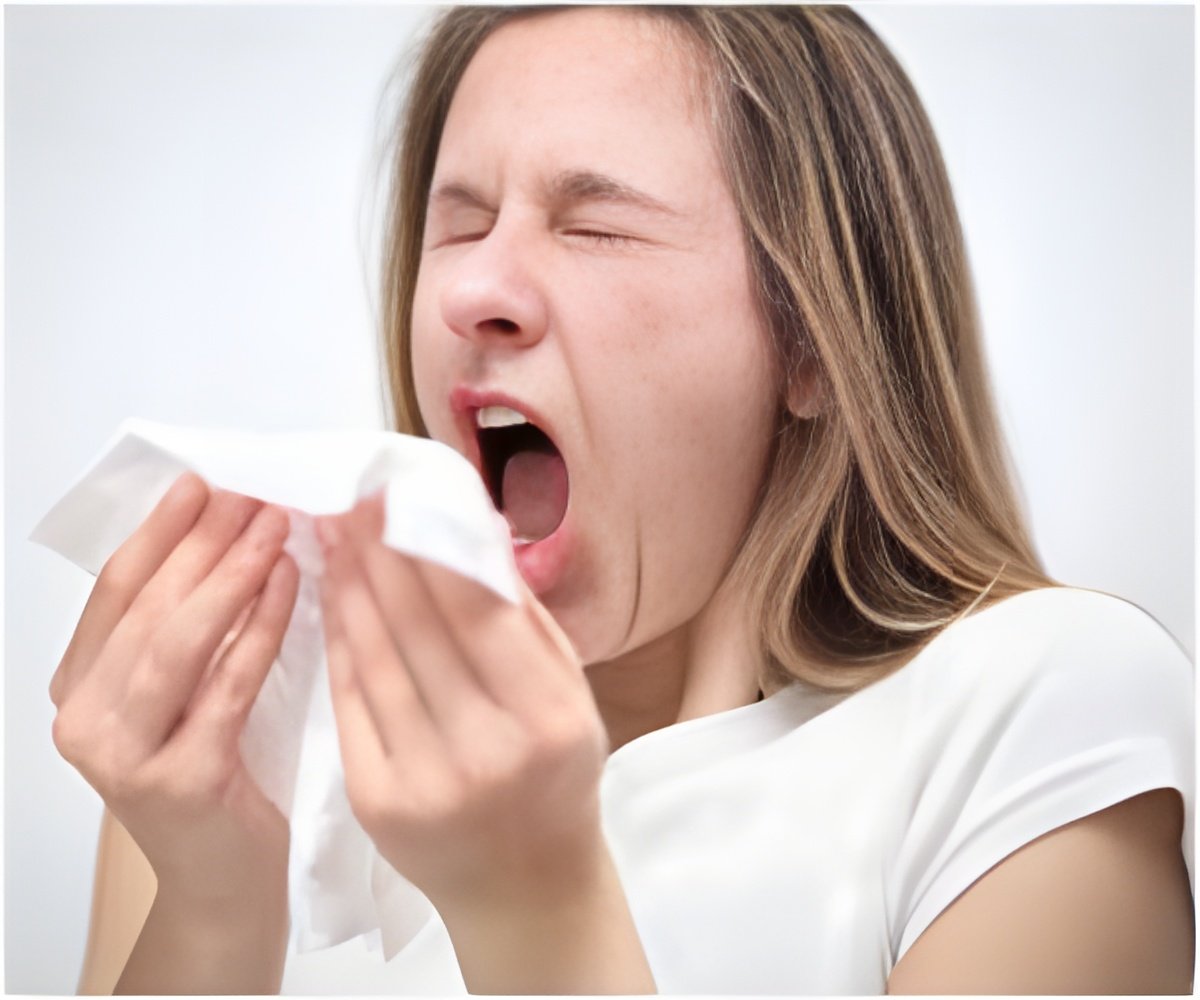
The ingestible or inhalable antibody prevents allergic reactions and asthma in adults, by binding to molecules which would otherwise cause allergy.

TOP INSIGHT
The antibody interacts in a complex biochemical process in the human body by which it prevents the human allergy antibody (IgE) from attaching to cells, thus keeping all allergic symptoms from occurring.
When exposed to external allergens, an allergic person produces high levels of IgE molecules.
The function of the antibody is that it interferes with binding of IgE to the two specific effector (CD23 and FceRI) on the immune cells, thereby making it impossible for the allergy molecule to bind.
Furthermore, the scientists have observed that the antibody also removes the IgE molecules even after binding to its receptors.
"Once the IgE on immune cells can be eliminated, it doesn't matter that the body produces millions of allergen-specific IgE molecules. When we can remove the trigger, the allergic reaction and symptoms will not occur," Spillner said.
The research team has conducted ex vivo experiments with blood cells from patients allergic to birch pollen and insect venom. However, the method can be transferred to virtually all other allergies and asthma, they said.
"It is a so-called single domain antibody which easily produced in processes using only microorganisms. It is also extremely stable, and this provides new opportunities for how the antibody can be administered to patients," Spillner said.
Source-IANS
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA




 Email
Email