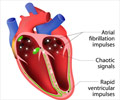
Atrial fibrillation (AF) can often be asymptomatic, leading to difficulties in diagnosis and untreated risks for morbidity and mortality.

‘Atrial fibrillation (AF) can often be asymptomatic, leading to difficulties in diagnosis and untreated risks for morbidity and mortality.’





In an analysis of a sustained AF (SAF) group, the prevalence of major comorbidities and stroke risk were comparable in both asymptomatic and symptomatic patients. According to lead author Masahiro Esato, MD, PhD, of the Department of Arrhythmia, Ijinkai Takeda General Hospital, Japan, "Although asymptomatic AF is common in daily 'real-world' clinical practice, the relationship between patient characteristics/clinical outcomes and symptom presentation has not been consistent across studies and therefore remains controversial. Our study was designed to shed light on this relationship." He notes that no detailed recommendation for asymptomatic AF management has been described, even in the latest AF guidelines.
Using data from the Fushimi AF Registry, a community-based prospective survey of patients with AF who visited the participating medical institutions in Fushimi-ku, Japan, researchers investigated the clinical characteristics and outcomes of asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with PAF (1,837 patients) and SAF (1,912 patients). In the PAF group, 689 were asymptomatic; while in the SAF group, 1,282 were asymptomatic. Median follow-up was 1,099 days.
Baseline clinical characteristics of all patients were collected, including a history of stroke or systemic embolism, heart failure, diabetes mellitus, heart failure, hypertension, and other medical conditions, as well as assessment stroke risk factor scores for patients with nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation. Use of oral anticoagulants and other drug therapies was also tracked.
The clinical characteristics and outcomes of asymptomatic AF patients were different between the PAF and SAF groups. During the follow-up period, the investigators found that all-cause mortality was higher in asymptomatic than symptomatic patients but only in the PAF group. This study also found poorer clinical outcomes in asymptomatic patients compared with the clinical outcomes of symptomatic patients in the PAF group but not in the SAF group.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert