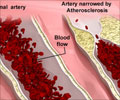
Researchers of University of California have recently discovered that a protein Nrf2, plays a vital role in some antioxidant therapies and also promotes atherosclerosis - clogging of arteries.
The protein, Nrf2, has been thought to be an important drug-therapy target for diseases such as cancer because it can induce chemo-preventive activity, leading to the release of numerous antioxidant and anti-inflammatory genes and enzymes. Earlier, researchers had reasoned that Nrf2, with its potent ability to boost antioxidants, might also be useful in combating the cell and tissue damage, or oxidation that leads to atherosclerosis.
However, UCLA scientists found that while Nrf2 boosted antioxidant properties in an animal model, it also increased the development of atherosclerosis by raising plasma cholesterol levels and cholesterol content in the liver.
According to them, this is the first study to document these additional effects on cholesterol metabolism in tandem with plaque formation in the arteries.
"The atherosclerosis-producing factors were greater than the antioxidant benefits. The development of novel antioxidant therapies is quite important, and this research may help shed light on why treatments affecting this protein may not be as effective as we thought," said principal investigator Jesus Araujo.
For the study, the team isolated and identified Nrf2's actions by looking at what would happen in mice that were specially bred without the protein.
They found that male mice without Nrf2 not only had decreased levels of antioxidants, but also exhibited a 53 percent reduction in atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta, compared with normal animals.
They also found that the mice without any Nrf2 had lower levels of total cholesterol in the blood and lower amounts of cholesterol in the liver.
In addition, the researchers found that most of the effects of Nrf2 were more highly prevalent in the male mice.
The study is published in the current issue of the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email