Glossary
Mutations: Any change in the DNA of a cell. Mutations may be caused by mistakes during cell division, or they may be caused by exposure to DNA-damaging agents in the environment. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect.DNA: The abbreviation for "deoxyribonucleic acid," the primary carrier of genetic information found in the chromosomes of almost all organisms.
Dioxin: They are a group of polyhalogenated organic compounds that are significant environmental pollutants.
Phenoxyacetic herbicides: Phenoxy herbicides are a family of chemicals related to the growth hormone indoleacetic acid (IAA) used to induce rapid, uncontrolled growth in plants but were later on banned as they contained dioxins.
Vinyl chloride: A substance used in manufacturing plastics. Exposure to vinyl chloride may increase the risk of liver, brain, and lung cancers; lymphoma; and leukemia.
Lymphoma: A group of cancers of the lymph nodes and spleen that can spread to other parts of the body.
Malignant: A cancerous growth that may destroy nearby normal tissue and spread to other parts of the body.
Benign: Not cancerous; does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body
Metastasis: Spread of a cancer from one organ or part of the body to another.
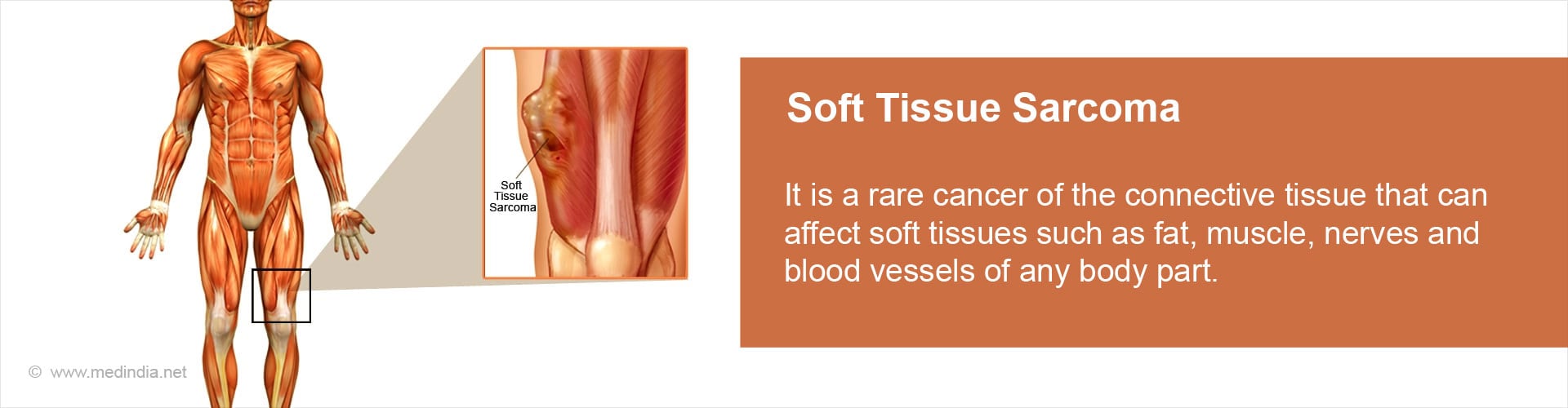
Sarcoma: A cancer of the bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels or other connective or supportive tissue.
Carcinoma: Cancer that begins in tissues lining or covering the surfaces (epithelial tissues) of organs, glands, or other body structures. Most cancers are carcinomas.
Lymph node: Round, oval or bean-shaped aggregation of infection- and cancer-fighting immune cells located along the lymph channels throughout the body.
Oncogene: Genes present in normal cells that, upon exposure to cancer-inducing factors may lead to development of tumors.
Tumor suppressor gene: Genes in the body that can suppress or block the development of cancer.