- Kodandapani S, Shreshta A, Ramkumar V, Rao L. Chorioangioma of Placenta: A Rare Placental Cause for Adverse Fetal Outcome. Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2012 (2012), Article ID 913878 - (http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/913878)
- Jiang H, Liu Y and Sun M. (2015) Severe Anemia and Thrombocytopenia in a Premature Associated with a Large Placental Chorioangioma. Open Journal of Pediatrics, 5, 45-48. doi - (10.4236/ojped.2015.51009.)
- García-Díaz L, Carreto P, Costa-Pereira CS and Antiñolo G. Prenatal management and perinatal outcome in giant placental chorioangioma complicated with hydrops fetalis, fetal anemia and maternal mirror syndrome. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2012, 12:72; doi - (10.1186/1471-2393-12-72)
- Prakashini PMV, Venkatesha S, Ramkumar V. Chorioangioma-A Rare Case of Polyhydramnios: A Case Report. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. Volume 4, Issue 8, 1095-1100. - (10.1186/1471-2393-12-72)
What is Chorioangioma?
Chorioangioma is a benign tumor of the placenta.
The placenta is a tissue that is attached to the inner lining of the uterus in pregnancy. Nutrients pass through the placenta and the attached umbilical cord from the mother to the fetus. The placenta also removes waste products from the fetus. It consists of two parts – the fetal side which is known as the chorionic plate and the maternal side which is called the basal plate. The chorion contains finger-shaped processes called villi. The villi contain connective tissue and blood vessels, which receive blood from the fetal circulation through the umbilical artery.
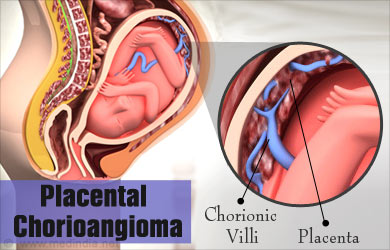
Chorioangiomas arise from the chorion tissue of the placenta. They may be single or multiple, small or large. Depending on the type, they may be classified as angiomatous which are rich in blood vessels, cellular which have fewer blood vessels, and degenerate.
What are the Causes of Chorioangioma?
There is no definite known cause of chorioangioma. However, certain conditions could possibly increase the chances of developing chorioangioma. These include:
- Older age of the mother
- Low oxygen levels caused by high altitudes
- Multiple pregnancies
- Female baby
- Diabetes or hypertension in the mother
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Chorioangioma?
Small chorioangiomas may not cause any symptoms and may even go undetected until delivery. In other cases, chorioangiomas may cause problems in pregnancy for the mother as well as the baby.
Possible complications of chorioangioma in the mother include:
- Polyhydramnios, where there is excess fluid in the amniotic sac surrounding the fetus.
- Preterm labor, resulting in an immature baby
- Preeclampsia, which is a condition characterized by high blood pressure, loss of protein in the urine, and fluid retention. Preeclampsia could progress to eclampsia, where the mother suffers from seizures
- Placental abruption, or separation of the placenta from the wall of the uterus
- Excessive bleeding
- Problems with clotting of blood
Chorioangioma may be associated with complications in the fetus. These include:
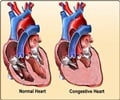
- Heart failure
- Hydrops fetalis, or accumulation of fluid in the fetus
- Hemolytic anemia, where there is breakdown of red blood cells
- Birth defects
- Low platelet count
- Restricted growth of the fetus
- Clotting disorders in the baby
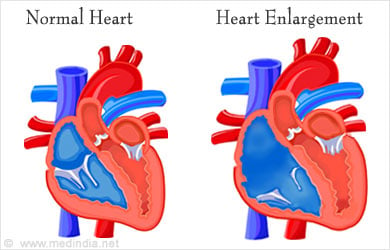
- Enlargement of the heart
How is Chorioangioma Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of chorioangioma is made through ultrasound. Ultrasound is considered as a safe radiology test during pregnancy and is therefore a preferred imaging test. A color Doppler test, which studies the blood flow through the tumor, is useful in conditions where a definite diagnosis with ultrasound is difficult.
How do you Treat Chorioangioma?
Chorioangioma that does not cause complications may not require treatment. If it is detected close to the delivery date, an early delivery should be planned. If it is detected earlier in pregnancy, the pregnancy should be carefully monitored to detect any complications at the earliest. Since the fetal lungs are not mature before 34 weeks, steroids may need to be administered to the mother to increase maturity of the lungs if a very early delivery is required.
Treatment modalities for chorioangioma include the following:
- Multiple fetal blood transfusions within the uterus to treat anemia and low platelet counts
- The blood flow to the feeding blood vessel of the tumor can be blocked during pregnancy using procedures like laser, absolute alcohol, etc.
- Treatment of associated conditions like polyhydramnios (excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid)
How do you Prevent Chorioangioma?
Since there is no specific cause for chorioangioma, its occurrence cannot be prevented. However, careful monitoring following its detection can detect any early complications early.