Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who had a certain gene variant experienced a higher incidence and severity of peripheral neuropathy after treatment with vincristine.
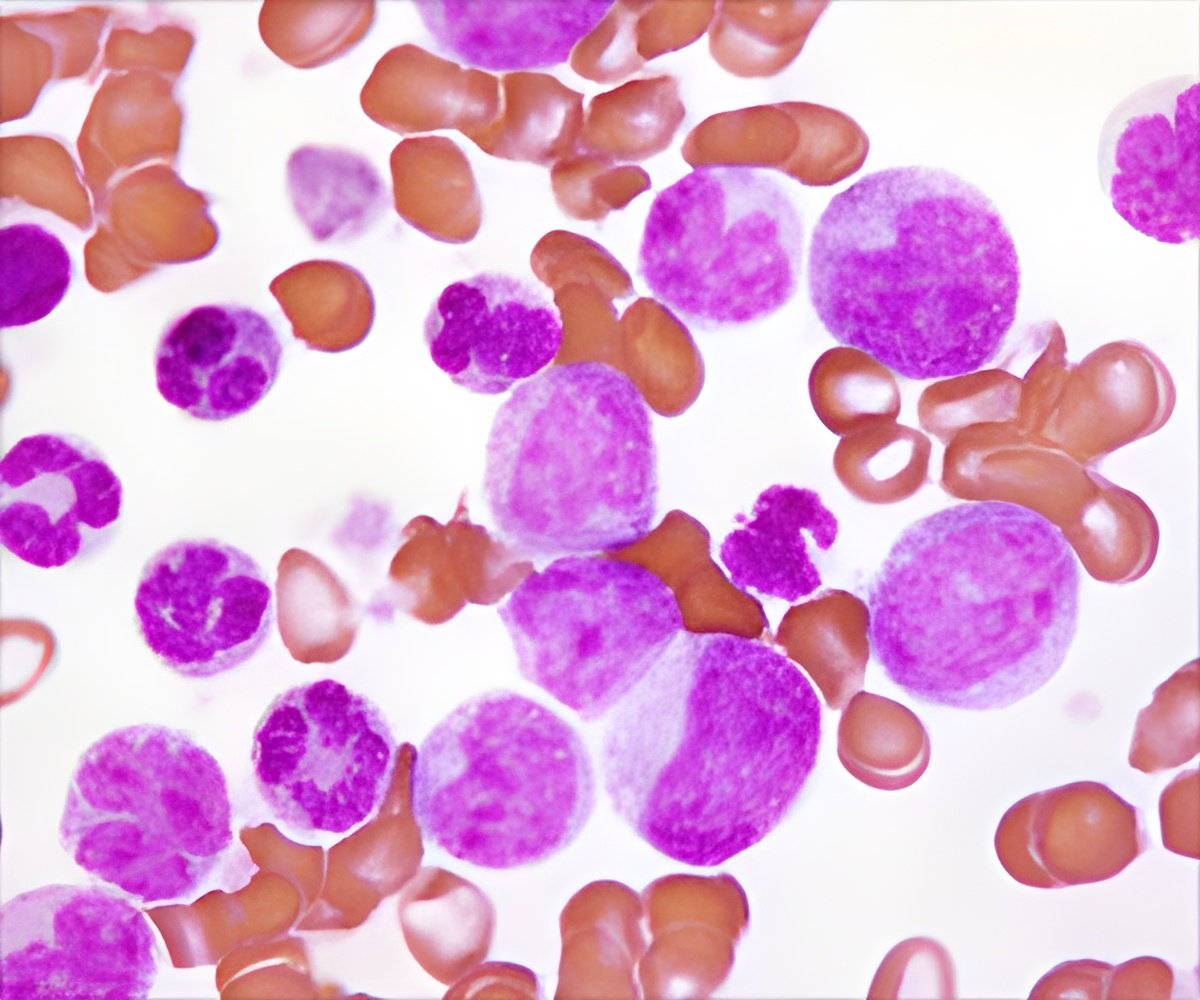
Researchers performed a genome-wide association study to determine whether there are genetic variants associated with vincristine-induced neuropathy. The study included participants in 1 of 2 prospective clinical trials for childhood ALL that included treatment with 36 to 39 doses of vincristine. Genetic analysis and vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy were assessed in 321 study patients from whom DNA was available- 222 patients (median age, 6.0 years) enrolled in 1994-1998 in a St. Jude Children's Research Hospital cohort; and 99 patients (median age, 11.4 years) enrolled in 2007-2010 in a Children's Oncology Group (COG) cohort.
Grade 2 (moderate) to grade 4 (life threatening) vincristine-induced neuropathy during therapy occurred in 28.8 percent of patients (64/222) in the St. Jude cohort and in 22.2 percent (22/99) in the COG cohort. The researchers found that an inherited variant in the gene CEP72 was associated with a higher incidence and severity of the cancer drug-related peripheral neuropathy in children with ALL. Among patients with the gene variant, 28 of 50 (56 percent) developed at least 1 episode of grade 2 to grade 4 neuropathy, compared with 21 percent (58/271) of other patients.
The authors wrote, "If replicated in additional populations, this finding may provide a basis for safer dosing of this widely prescribed anticancer agent."
The study is published in the 'JAMA'.
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email