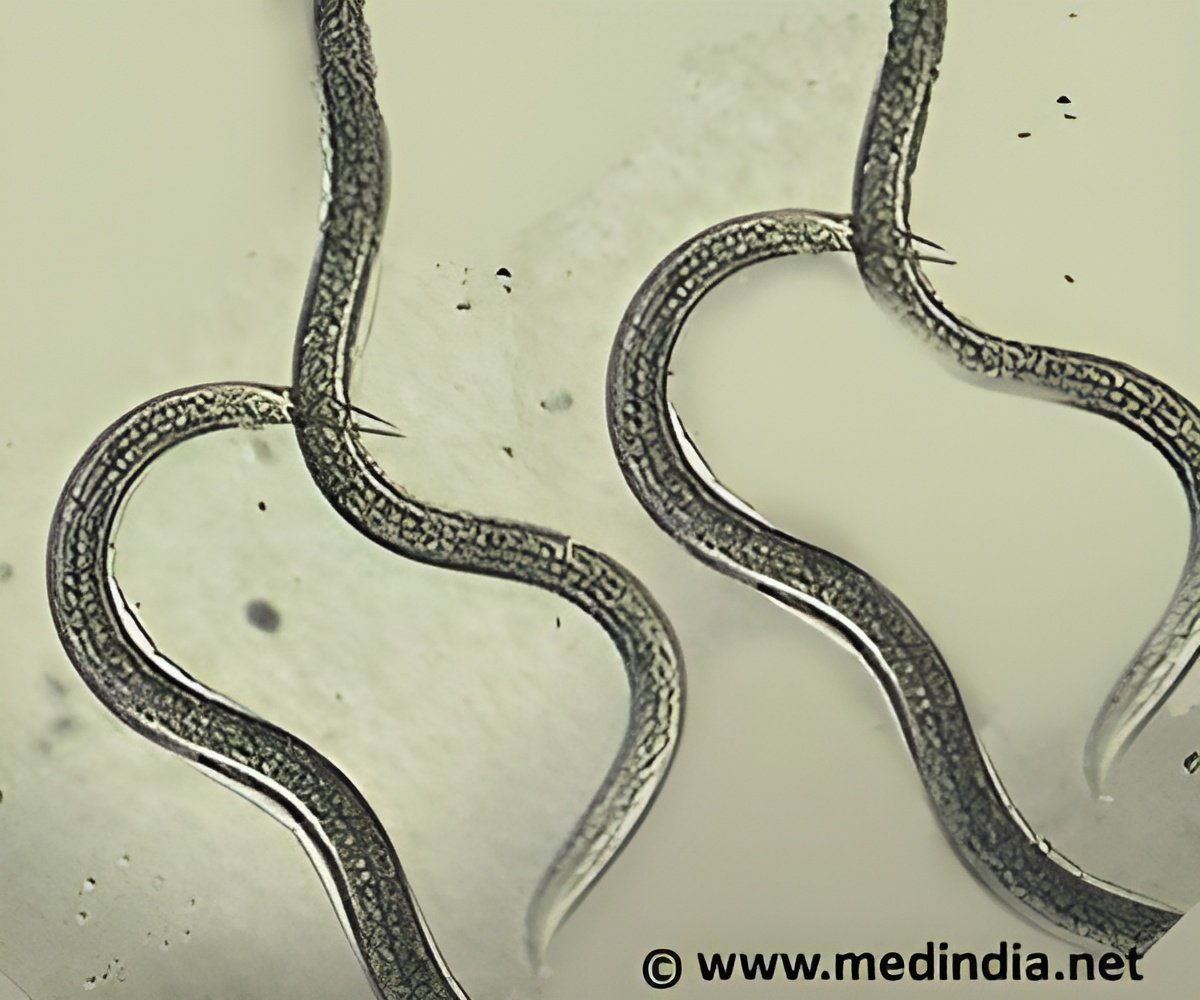
The three-banded panther worms closely resembling plump grains of wild rice set in motion, swimming in disposable containers in hardly seemed like the next big thing in regeneration.
"It was a big risk for us—it was not a project where you knew it was going to work from the beginning," says Reddien, who is also an associate professor of biology at MIT and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Investigator. "I had no idea how successful we'd be with culturing the animals or how successful the methods for development would be. There are all kinds of ways we could've failed on this one, but it was fun. It's the kind of science that has an adventurous spirit to it. And the organism is an even better model organism than we could have hoped for."
Reddien and Srivastava present their new model to the scientific community in the May 19th issue of the journal Current Biology.
Once the worms arrived in their new home in Cambridge, the first test was to acclimate them to lab life and determine their needs for survival. Initially, the worms were dying. The salinity of their water was off, even though it matched the pond where they were found. Hofstenia also rejected the liver that is the dietary mainstay for Reddien's other model of regeneration, the planarian (Schmidtea mediterranea). The three-banded panther worms shrank in size and some resorted to cannibalism.
Eventually, the water quality was fixed and a preferred food source was identified: sea monkeys, also known as brine shrimp. Now the worms are thriving and laying numerous eggs, enough to create an ample supply of animals for experiments.
Through a series of dissections, Reddien and Srivastava established that Hofstenia not only regenerate their heads, but, like planarians, are also able to regrow any body part. The scientists then documented the worm's transcriptome—a list of all of the genes that are transcribed in the animal—and established that RNA interference (RNAi) could be used in this animal to inhibit specific genes and unlock the molecular functions that allow regeneration.
If Hofstenia and planarians were phylogenetically close, such similarities would not be surprising. But after analyzing the Hofstenia transcriptome, the team determined that the three-banded panther worm and planarians are only very distantly related, a view that had been proposed based on analyses with sequences from a small number of genes.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email




