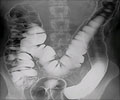
A team of authors have claimed that current guidelines of colorectal cancer screening for people who have first-degree relatives with precancerous colon polyps are not effective
Current guidelines for people who have first-degree relatives with precancerous polyps range from those of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, which makes no specific screening recommendation, to the guidelines of the American Cancer Society and the American College of Gastroenterology, which recommend a colonoscopy starting at age 40, or 10 years younger than the earliest diagnosis in the family (whichever comes first), and repeated every five years if the first-degree relative was diagnosed with a precancerous lesion before age 60.
The study, "Risk for Colorectal Cancer in Persons With a Family History ofAdenomatous Polyps" appears in the May 15 issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine. The systematic review was supported by the National Cancer Institute. David F. Ransohoff, M.D., of the University of North Carolina co-authored the paper with Dr. Imperiale.
"This is another important reason to know your family's health history," Dr. Imperiale said. "Until there is better evidence available, we suggest talking with your primary care physician and basing the decision on whether and how to be screened on the age of the youngest first-degree relatives with precancerous polyps and whether the precancerous polyps are classified as advanced or not."
A third to a half of Americans who undergo a colonoscopy are found to have one or more precancerous polyps, according to Dr. Imperiale, so it is extremely common to have a first-degree relative with a precancerous polyp. However, only 5 to 10 percent of these growths are advanced.
Until new, rigorous studies inform screening guidelines, Dr. Imperiale recommends an initial screening colonoscopy if the first-degree relative was younger than 60 and the polyp was advanced when found. If a first-degree relative was 60 or older when the advanced polyp was found, or any age when nonadvanced polyps were detected, he suggests that the family member be screened as average risk. Average-risk options include a high-sensitivity stool blood test annually or a colonoscopy every 10 years.
NCI estimates that 51,690 men and women will die of cancer of the colon and rectum in 2012.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email