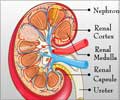
Every year acute renal failure affects over 13 million people and leads to 1.7 million deaths across the globe.
TOP INSIGHT
Deactivating the NF-kappaB molecule specifically in the renal tubular epithelial cells leads to less tissue damage and necrosis during an ischemia.
NF-kappaB is a transcription factor: a molecule that activates genes, and in other tissues those genes are associated with functions such as programmed cell death, inflammations and immune responses. Because it has so many important tasks in the body, simply targeting the protein with drugs is usually not an option for treatment.
But the scientists' work has now brought the molecule back into play. "We developed a unique mouse model in which we deactivated the NF-kappaB molecule very specifically in renal tubular epithelial cells," says Dr Markó;. Following an artificially induced case of ischemia, these mice experienced considerably less tissue damage and necrosis, and had far fewer sites of inflammation than control animals. The loss of NF-kappaB reduced the activity of its normal target genes in the kidneys. And in laboratory cultures of tubular cells, suppressing the signaling pathway allowed more cells to survive while reducing the release of inflammatory factors.
The scientists hope that tracing ischemia's effects to NF-kappaB activity in a specific type of cell might be a first step toward developing a future therapy tailor-made to target it. And the strain of mouse developed for the project can be used to study the activity of other proteins in tubular cells, providing a way to study other kidney diseases that affect them.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email