Chemical (S)-N'-nitrosonornicotine or (S)-NNN, which is found in smokeless tobacco products, is a powerful oral carcinogen, aver scientists.
"(S)-NNN is the only chemical in smokeless tobacco known to cause oral cancer," Balbo said.
"This finding provides mechanistic underpinning for the epidemiologic observations that smokeless tobacco products cause oral cancer," she added.
Balbo and colleagues administered two forms of NNN called (S)-NNN and (r)-NNN to four groups of 24 rats. The rats were given either (S)-NNN alone, (r)-NNN alone, a combination of both or tap water. The total dose was approximately equivalent to the amount of (S)-NNN to which a smokeless tobacco user would be exposed from chronic use of these products.
All rats assigned to (S)-NNN alone or the combination began losing weight after one year of exposure and died by 17 months. Rats assigned to (r)-NNN or tap water were terminated at 20 months.
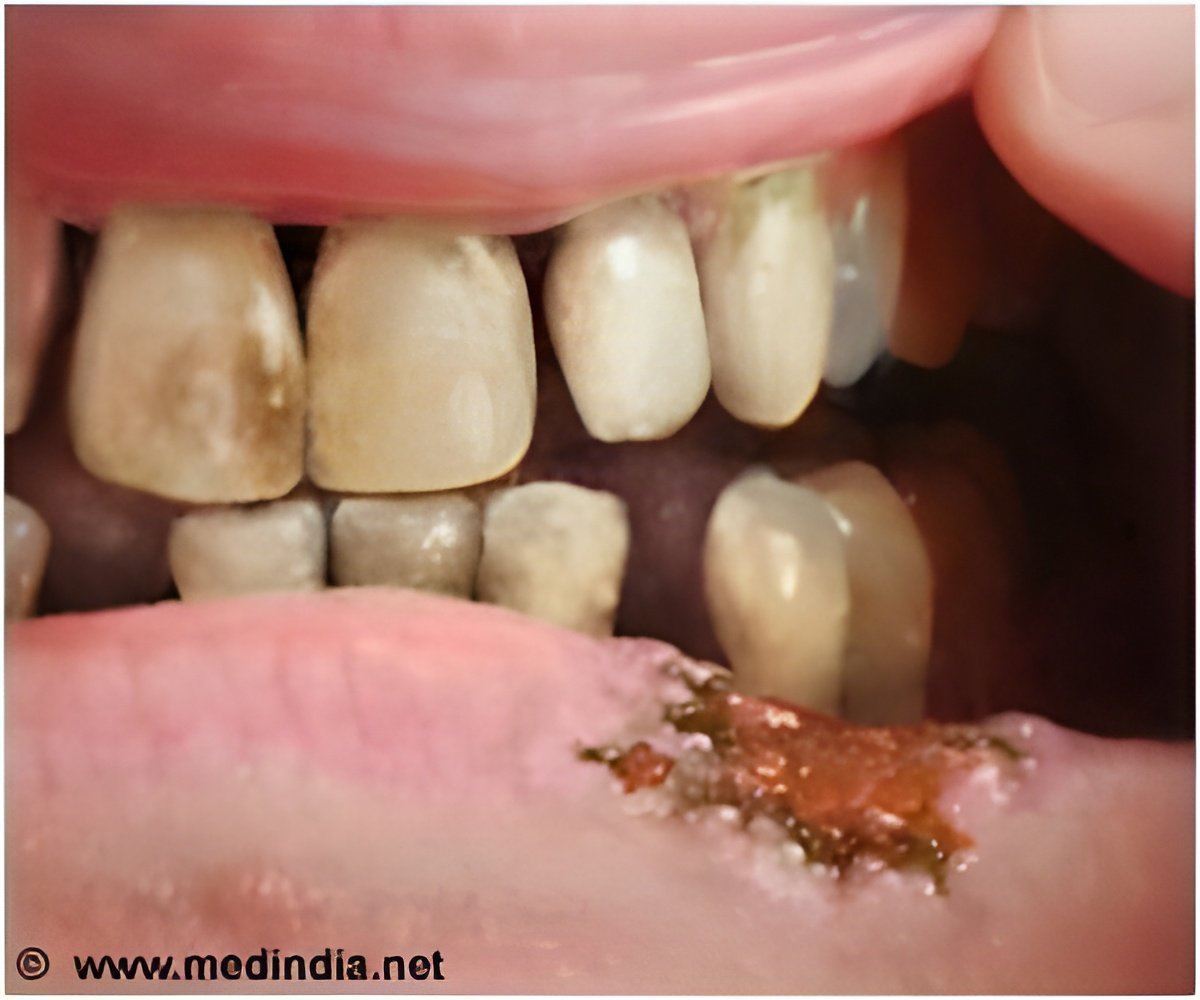
All rats assigned to (S)-NNN had esophageal tumors and demonstrated 100 percent incidence of oral tumors including tumors of the tongue, buccal mucosa, soft palate and pharynx.
"Measures should be taken to reduce this chemical in smokeless tobacco. If it is not possible to stop the use of smokeless tobacco products, we should advocate for a reduction of this chemical in these products," Balbo said.
"In addition, we have to understand how this research translates to human beings. We have to understand the uptake of NNN from smokeless tobacco products in humans and develop better biomarkers, such as urinary biomarkers, to have a tool to monitor the levels to which smokeless tobacco users are exposed," Balbo added.
Balbo believes these findings are yet another affirmation that tobacco products should be avoided.
The finding was presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2012, held March 31 - April 4.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email