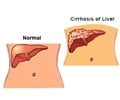
The researchers found that those who were obese but did not drink were 1.7 times more likely to develop liver disease compared to those who were thin and did not consume any alcohol. The risk increased to 1.8 times among those who were thin and drank alcohol while it was the highest, at three times, among those who were obese and drank alcohol.
“It's well known that alcohol and a person's weight are major causes of chronic liver disease, but there has been a need for a large population study to compare these factors' influences on each other. Interestingly, the research found the combination of a woman's drinking habits and weight has an important effect on liver health and life expectancy”, European Association for the Study of the Liver Committee’s Dr Daniele Prati said.
Source-Medindia