A new radiotherapeuti drugs may bring new hopes for patients suffering from metastatic prostate cancer that failed to respond to hormone deprivation drugs
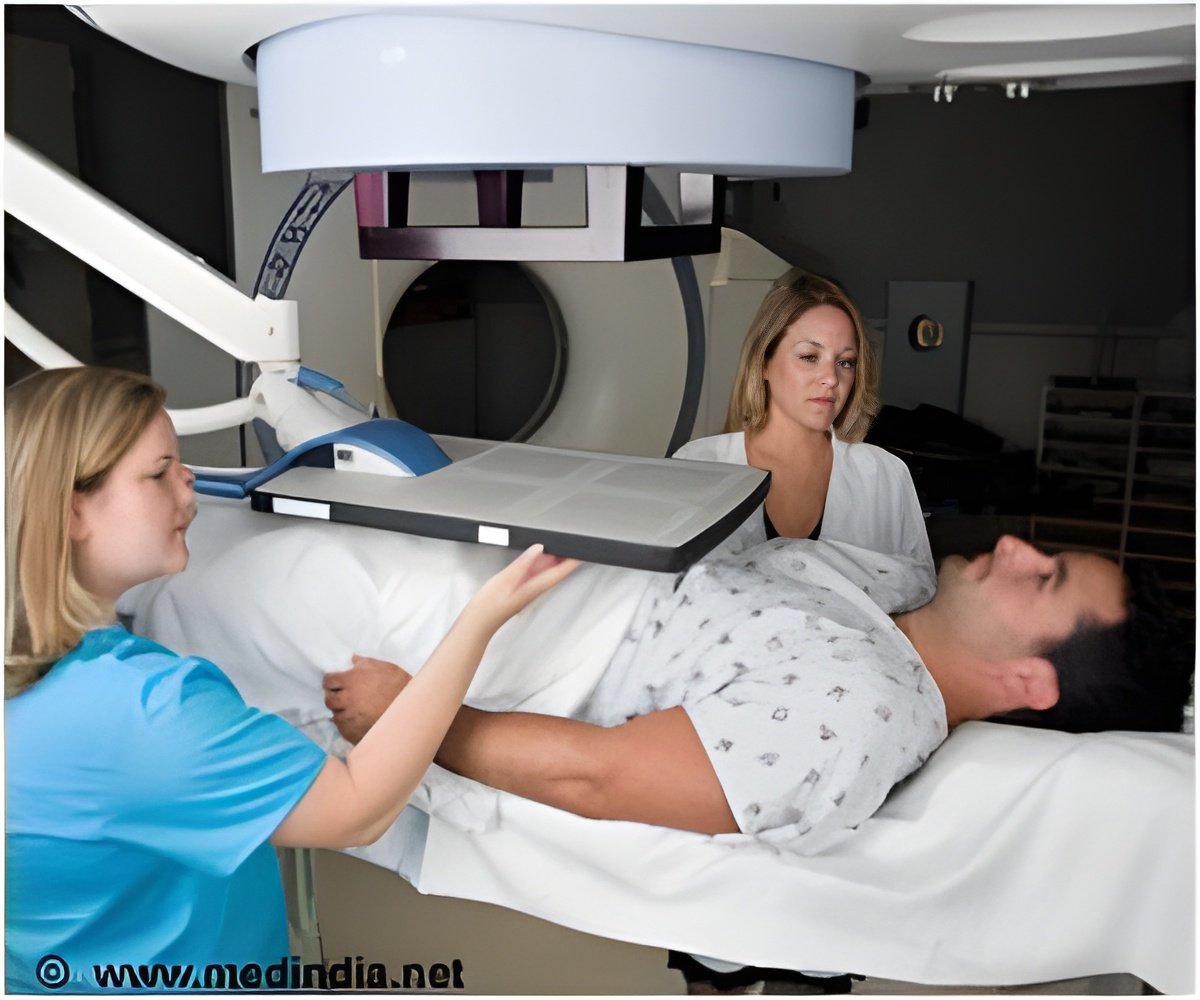
Radium-223, a radiotherapeutic drug sold under the brand name Xofigo, is the first apha particle emitter to undergo phase 3 testing and, in May, to receive FDA approval for use in the United States. In the editorial, "Fighting Prostate Cancer with Radium-223 - Not your Madame's Isotope," Vapiwala and her co-author, Eli Glatstein, MD, the Morton M. Kligerman Professor of Radiation Oncology at Penn, highlight the therapy's "winning combination." It mimics calcium and homes in on places where tumors have formed in the bones, and the alpha-emitter is potent enough to damage cancer cells' DNA in "a single knockout," unlike x-ray radiation therapy that must be delivered for many days and weeks in a row to be most effective.
"The real-world applicability of this new therapy is undeniable," Vapiwala says. "Hormone-refractory prostate cancer that has metastasized to the bones can be a debilitating and, in many cases, life-threatening battle. The addition to our armamentarium of this well-tolerated, bone- targeted therapy that helps to not only relieve symptoms but also extend lives is an incredibly important development for the 30,000 men who are facing death from prostate cancer each year, and for all of the individuals who care for them. It is also a seminal event in the realm of alpha-emitter therapy, opening a new door for more research into this class of agents that has great potential in other areas of oncology."
Importantly, Radium-223's safety is enhanced by a short half-life of only 11.4 days, which limits the toxicity historically observed with radium exposure. The dangers of radium are perhaps most well known from the story of female factory workers who suffered severe radiation poisoning after from painting watches with radioactive, glow-in-the-dark paint during the early 20th century. Believing the paint was safe, the women ingested it by licking their brushes to maintain a fine point while painting the watch dials.
Vapiwala's editorial explores the history of radium, the process by which radionuclide therapy has, in recent years, been coupled with targeted immunotherapies to seek and destroy tumors while sparing normal tissue, and looks to a future in which radiotherapeutic drugs may become even more useful. "As new targeting molecules emerge, we can envision alpha emitters as a potent partner to further enhance radioimmunotherapy and create the ultimate smart bomb," the authors write.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email