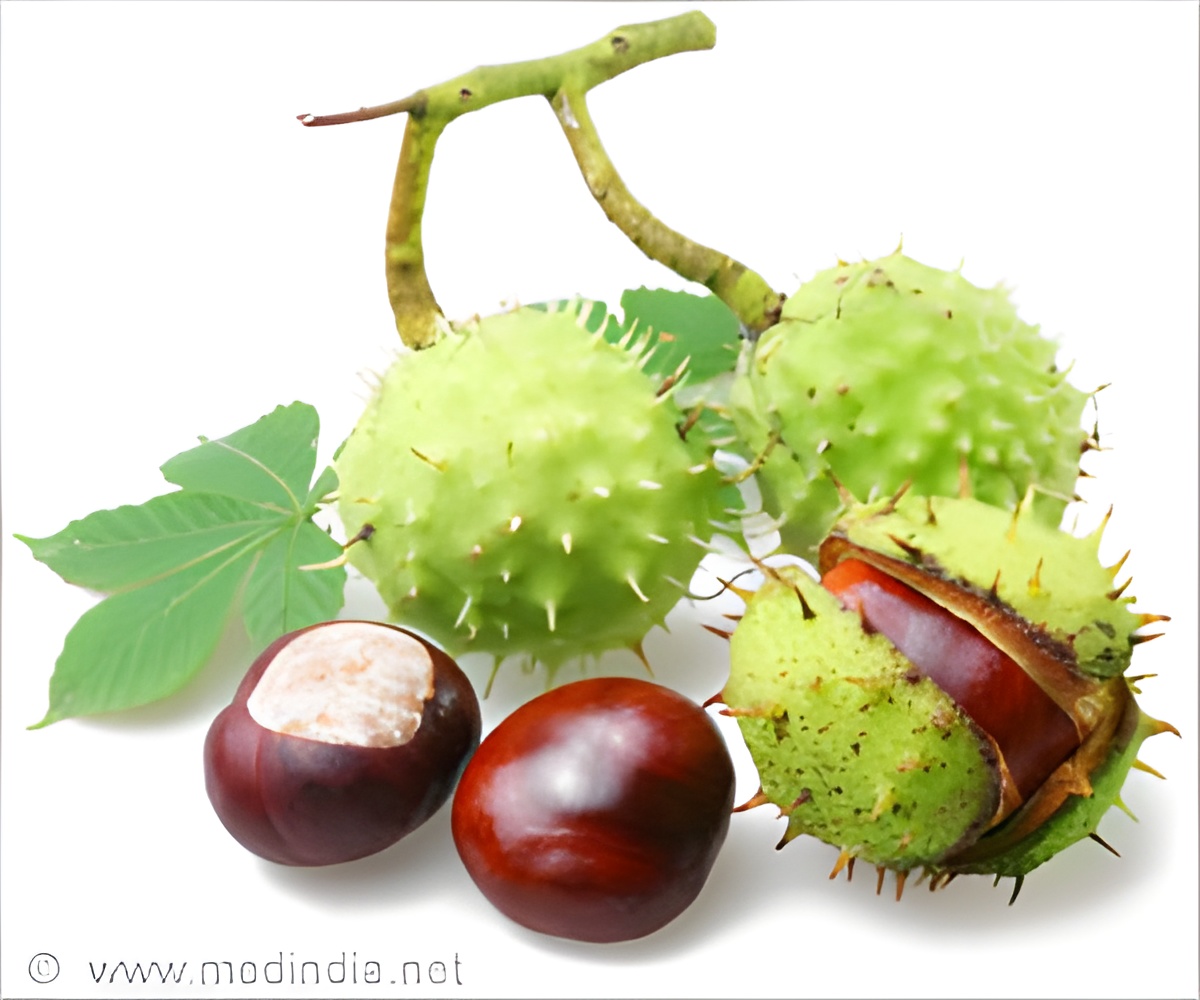
‘A radiation responsive esculin-derived molecular gel derived from horse chestnuts can help detect cancer better.’





The team has developed a radiation responsive esculin-derived molecular gel, that is both scintillating and fluorescent, to enhance the optical photon output in image mapping for cancer imaging.Esculin, or Æsculin, is a coumarin glucoside that naturally occurs in the horse chestnut, a plant extract. It is beneficial to circulatory health.
A challenge currently in cancer imaging is that optical imaging of radiotracers through Cerenkov light (the Grimm lab is one of the leading labs in this field) often produces light that is typically low in intensity and blue-weighted (greatly scattered and absorbed in vivo). It is therefore imperative to increase or shift the photon flux for improved detection.
The gel has been developed to address this challenge.
"Tailoring biobased materials to synthesize thixotropic thermo-reversible hydrogels offers image-aiding systems which are not only functional but also potentially economical, safe, and environmentally friendly," said John.
Advertisement
A Fellow of Britain's Royal Society of Chemistry, John's research is rooted in the idea that innovation can be inspired by nature to develop economical and green technologies for a sustainable future.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert