A molecule that plays a vital role in the breakdown of kidney filter, thereby leading to kidney failure, has been detected by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital.
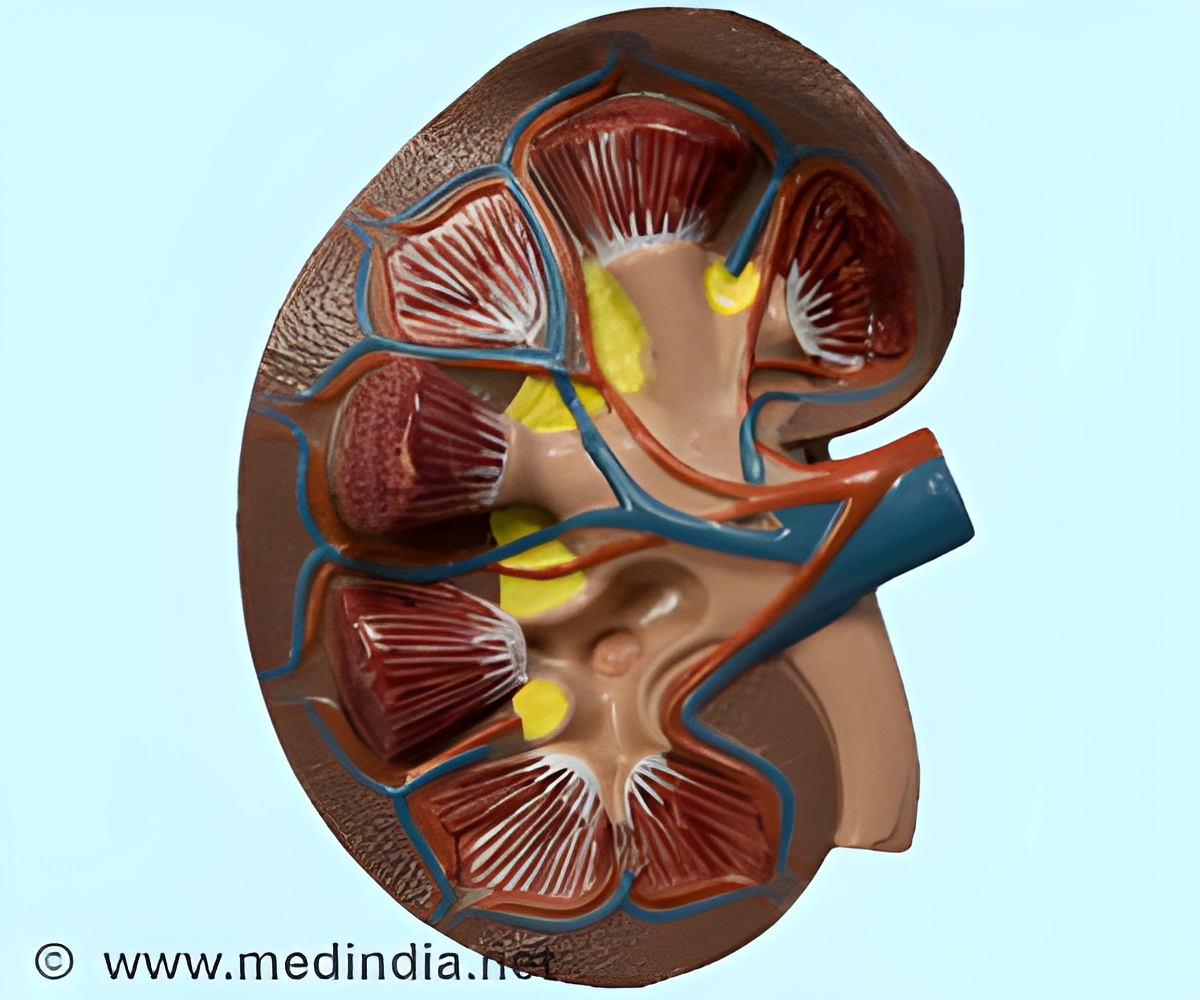
"Our study shows that blocking the ion channel TRPC5 may be a new treatment for diseases in which the kidney's filter barrier is damaged," says Anna Greka, MD, PhD, of the Division of Nephrology in the MGH Department of Medicine, who led the current study. "One in three Americans is at risk for developing chronic kidney disease from obesity, diabetes or high blood pressure; and kidney failure has been described as an emergent pandemic of our time."
TRPC5 is an ion channel, a pore in the cell membrane that transmits metabolic signals by allowing charged molecules – in this case calcium – to pass into or out of cells. Disrupted calcium signaling was suggested as a possible early event in damage to podocytes – the cells that make up the kidney's filter barrier – several decades ago, but the particular calcium channel that was involved had never been identified. Some families with a rare, inherited form of kidney disease were known to have activating mutations in a related calcium channel called TRPC6, which led Greka's team to investigate its role in kidney filtration. They were surprised to find that, in addition to TRPC6 channels, TRPC5 channels were also present in podocytes and that their activity was more damaging to the kidney filter, even in the absence of any mutations.
The current article describes a series of experiments by which Greka's team first confirmed the presence of TRPC5 channels in rodent podocytes; they then showed that animals in which TRPC5 expression was knocked out did not experience the type of kidney damage typically caused by a bacterial toxin or by a chemical known to damage podocytes. More detailed studies revealed that those damaging agents cause TRPC5 channels to open in podocytes, admitting excess calcium which causes the cytoskeleton – the cells' internal structural support system – to collapse, breaking down the filter formed by podocytes.
The researchers went on to show that a recently identified TRPC5 inhibitor, called ML204 – discovered in the lab of study co-author Craig Lindsley, PhD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center – blocked the inrush of calcium into podocytes, preventing cytoskeletal breakdown and the damage to the kidney's filtering function. This protective effect was seen not only in cells and tissues but also in living mice.
"Future work needs to focus on optimizing ML204 and other potential TRPC5 blockers to be more potent. But generally our intention is to fervently pursue TRPC5 inhibition as a possible new treatment for the kidney diseases affecting hundreds of millions of people worldwide," says Greka, who is an assistant professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email










