An effective method of exome-sequencing has the potential to help researchers identify genetic diseases in record time.

The exome-a small part of the genome- is of crucial interest with regard to research on genetic diseases as it accounts for 85 percent of mutations.
"With this new approach, we no longer need to access patients who share the same altered gene pools to be able to identify the gene responsible for a disease. All we require are two persons affected by the disease not necessarily from the same family," explained Jabado.
"Now, within two weeks and with just two patients, we can easily isolate a gene. This compares to a time frame of six or seven months or even years before we saw results with the old process. This is really a positive breakthrough in genetic analysis," he added.
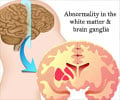
In the study, the researchers focused on isolating the mutation responsible for a rare and deadly genetic syndrome, Fowler's Syndrome, which is involved in the anarchic proliferation of brain vessels that hinder the brain's development.
Their results have revealed - between two patients with no family ties - a rare case of four mutations in the same gene.
Advertisement
"These results are very promising. There is now hope that in the near future we can treat a patient presenting a rare, unknown genetic disease in our laboratory, and within a few days be able to sequence his or her DNA to find the mutation that caused the disease," stated Dr. Jacek Majewski.
Advertisement
"The sequencing of genetic diseases will lead to a change in our medical practices. Each patient could receive a personalized treatment depending on the particular genes involved. By sequencing the patient's genome, we will be better able to target the disease and adapt treatment to achieve the best results, according to tolerance levels for each person," said Jabado.
The results of the study have been published in the journal Human Mutation.
Source-ANI