People suffering from gall bladder stones have increased chances of developing cardiovascular diseases down the road.
TOP INSIGHT
To prevent heart diseases associated with gallstones, measures such as maintaining gastrointestinal health, eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising and keeping blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol under control, will help.
To cardiologist Dr. Richard Stein, the study makes a “pretty convincing” case that gallstones, themselves, are a risk factor for heart disease. Stein, who wasn’t involved in the research, is director of the urban community cardiology program at New York University School of Medicine.
He said that people with a history of gallstones may want to pay extra attention to their cardiovascular health. “Eat a heart-healthy diet, exercise, keep your blood pressure down. It would be prudent to get your other heart disease risk factors under control,” said Stein, who is also a spokesperson for the American Heart Association.
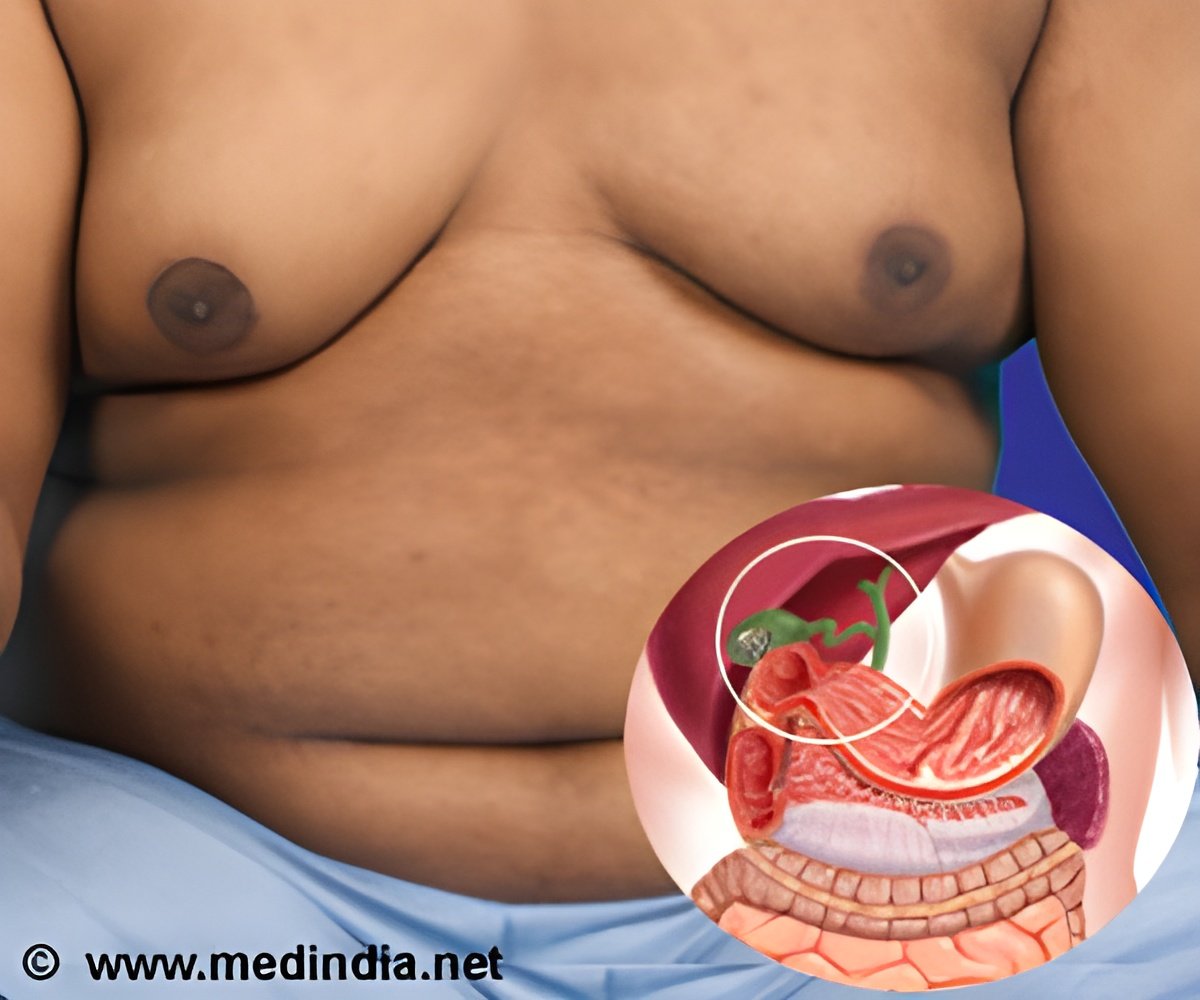
Gallstones are hard particles that develop in the gallbladder, a small organ that stores the bile fluids that help the body digest fat and fat-soluble vitamins. Gallstones form when there are imbalances in the substances that make up bile: Excess cholesterol is the usual suspect, according to the U.S. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK).
For many people, gallstones cause no symptoms, NIDDK says. But if they block a bile duct, they can cause abdominal pain. often after a heavy meal. Most often, treatment involves surgically removing the gallbladder.
In all, the studies followed more than 269,000 men and women for up to 30 years. Just over 6% of women and 3% of men said they had ever been diagnosed with gallstones.
The researchers then pooled those results with findings from four previous studies that included nearly 900,000 people. All together, they found that adults with a history of gallstones were 23% more likely to develop heart disease.
Although the study couldn’t prove a cause-and-effect relationship between gallstones and heart disease, Qi suggested that changes in the gut’s microbiome may play a role. That refers to the trillions of bacteria and other microbes that normally dwell in the digestive system. Gallstones can disrupt the balance of microbes in the gut, and recent studies have linked such disturbances to the risk of heart disease.
But, he stressed, that’s just a theoretical explanation for now. Stein speculated on another possibility. Some cases of gallstone disease might spur low levels of inflammation in the body that feed the development of heart disease. “We’ve known for years that chronic, low-grade inflammation is associated with heart disease,” Stein said.
Whatever the reasons for the link, Qi said it highlights a connection between the gastrointestinal and cardiovascular systems. “To help protect your heart health, you may also need to protect your gastrointestinal system,” he said.
There are certain risk factors for gallstones that you cannot change, according to NIDDK. People with a family history of them are at increased risk, for instance. Gallstones are also more common in women than men.
But some other factors, such as obesity, and diets high in fat and processed carbohydrates, can be changed, the institute suggests.
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email