Rising temperature due to climatic change may increase the number of infants born with congenital heart defects (CHD).
The number of infants born with congenital heart defects (CHD) in the United States might increase due to escalating temperature stemming from global climatic change. The impact might result in more than 7000 new cases of CHD over 11 years in eight representative states in the US, revealed research published in the
Journal of the American Heart Association.//
"Our findings underscore the alarming impact of climate change on human health and highlight the need for improved preparedness to deal the anticipated rise in a complex condition that often requires lifelong care and follow-up," said study senior author Shao Lin, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., professor in the School of Public Health at University of Albany, New York. "It is important for clinicians to counsel pregnant women and those planning to become pregnant on the importance of avoiding extreme heat, particularly 3-8 weeks post conception, the critical period of pregnancy."
TOP INSIGHT
Many animal studies have shown that excessive heat causes fetal cell death or interference with heat-sensitive proteins that are integral to fetal development.
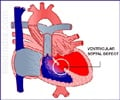
Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defect in the United States affecting some 40,000 newborns each year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
"Our results highlight the dramatic ways in which climate change can affect human health and suggest that pediatric heart disease stemming from structural heart malformations may become an important consequence of rising temperatures," said the leading author Wangjian Zhang, M.D., Ph.D., a post-doctoral research fellow at the University of Albany.
The projected increase in children with congenital heart disease will pose greater demand on the medical community caring for newborns with heart disease in their infancy and well beyond.
While previous research has found a link between maternal heat exposure and the risk for heart defects in the offspring, the precise mechanisms remain unclear. Studies in animals suggest that heat may cause fetal cell death or interfere with several heat-sensitive proteins that play a critical role in fetal development, the researchers say.
The estimates in the current study are based on projections of the number of births between 2025 and 2035 in the United States and the anticipated rise in average maternal heat exposure across different regions as a result of global climate change. The greatest percentage increases in the number of newborns with CHD will occur in the Midwest, followed by the Northeast and South.
In their analysis, the researchers used climate change forecasts obtained from NASA and the Goddard Institute for Space Studies. They improved the spatial and temporal resolutions of the forecasts, simulated changes in daily maximum temperatures by geographic region and then calculated the anticipated maternal heat exposure per region for spring and summer. For each pregnancy and region, they defined three exposure indicators: 1) the count of excessively hot days (EHD) as the number of days exceeding the 90th (EHD90) or 95th (EHD95) percentile for the same season of the baseline period at the same region; 2) the frequency of extreme heat events (EHE) as the number of occurrences of at least three consecutive EHD 90 days or two consecutive EHD 95 days; and 3) the duration of EHE as the number of days for the longest EHE within the 42-day period.
To obtain a parameter for congenital heart defect (CHD) burden projections, the investigators used data from an earlier study, also led by Lin, which gauged the risk of congenital heart defects based on maternal heat exposure for births occurring between 1997 and 2007. The researchers then integrated the heat-CHD associations identified during the baseline period with the projected increases in maternal heat exposure over a period between 2025 and 2035 to estimate the potential changes in CHD burden.
"Although this study is preliminary, it would be prudent for women in the early weeks of pregnancy to avoid heat extremes similar to the advice given to persons with cardiovascular and pulmonary disease during heart spells," said Shao Lin, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., associate director of environmental health services, University at Albany, State University of New York.
Source-Eurekalert

 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email










