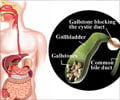
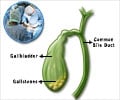
High doses of epsom salt prescribed to treat gallstones caused liver damage in a 38-year-old man.
TOP INSIGHT
Taking too much Epsom salts can cause diarrhea, abnormal heart rhythm, kidney damage and liver failure in the case of an already existing disease.
Taking too much Epsom salts can cause diarrhea, abnormal heart rhythm, and kidney damage.
In this case, the man took a large quantity of salts over two weeks, which prompted rapid worsening of fibrosis (tissue scarring). And the doctors caution that certain conditions might heighten the risk of liver damage when combined with Epsom salts.
The man was advised to stop taking the salts, to drink plenty of fluids, and was given medication to prevent further liver damage. And after around six weeks, his liver function had returned to normal.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email