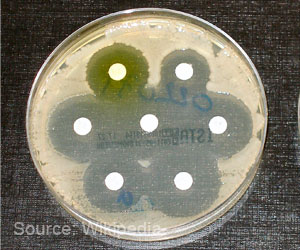
Continuing to use medically important antibiotics for growth promotion in animals is one main reason for antibiotic resistance to diseases.

TOP INSIGHT
Inappropriate use of drugs in animals is a leading cause of antimicrobial resistance. This can be used by limiting fast food intake, imposing fee on price of veterinary antibiotics and regulation of antibiotic use.
Three Ways To Reduce Antibiotics Use For Animals
In the Science study, researchers estimated the global impact of three interventions on reducing antibiotic use in animals. Together, these interventions could reduce animal consumption of antibiotics worldwide by up to 80 percent.
- Regulations capping the use of antibiotics in farm animals could achieve a 64 percent reduction in consumption.
- Limiting meat intake to the equivalent of one fast-food burger per person per day globally, could reduce antibiotic consumption in animals by 66 percent.
- Imposing a 50 percent user fee on the price of veterinary antibiotics could reduce consumption by 31 percent while generating revenues of US $ 1.7 billion to $4.6 billion per year, which could be used to spur drug development.
Globally, more than 131,000 tons of antibiotics were used in animals in 2013, the researchers found. By 2030, projected consumption will increase to more than 200,000 tons. The current top five users of antibiotics in food production, by country, are China, United States, Brazil, India, Spain. The projected intake of antibiotics may increase between 6 to 82% by 2030.
In 2016, the meeting on antimicrobial resistance (AMR) at the United Nations General Assembly recognized the inappropriate use of these drugs in animals as a leading cause of rising AMR.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email