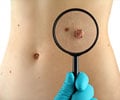
Be careful if you are consuming a lot of whole grapefruit and orange juice. It may increase your risk of melanoma, say cancer researchers at Brown University.

Consumption of grapefruit and oranges was not associated with an increased risk for any other non-skin cancers.
"While our findings suggest that people who consume large amounts of whole grapefruit or orange juice may be at increased risk for melanoma, we need much more research before any concrete recommendations can be made," said lead study author Shaowei Wu, postdoctoral research fellow at Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island.
"At this time, we do not advise that people cut back on citrus -- but those who consume a lot of grapefruit and/or orange juice should be particularly careful to avoid prolonged sun exposure," Wu noted.
The apparent link between melanoma and citrus fruit consumption may be due to high levels of substances called furocoumarins found in citrus fruits, the researchers pointed out.
Prior research showed that furocoumarins make the skin more sensitive to sunlight, including to melanoma-causing ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Advertisement
Higher overall citrus fruit consumption (the total number of servings of whole grapefruit, whole oranges, and juices from those fruits) was associated with increased risk of malignant melanoma in both men and women.
Advertisement
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Source-IANS