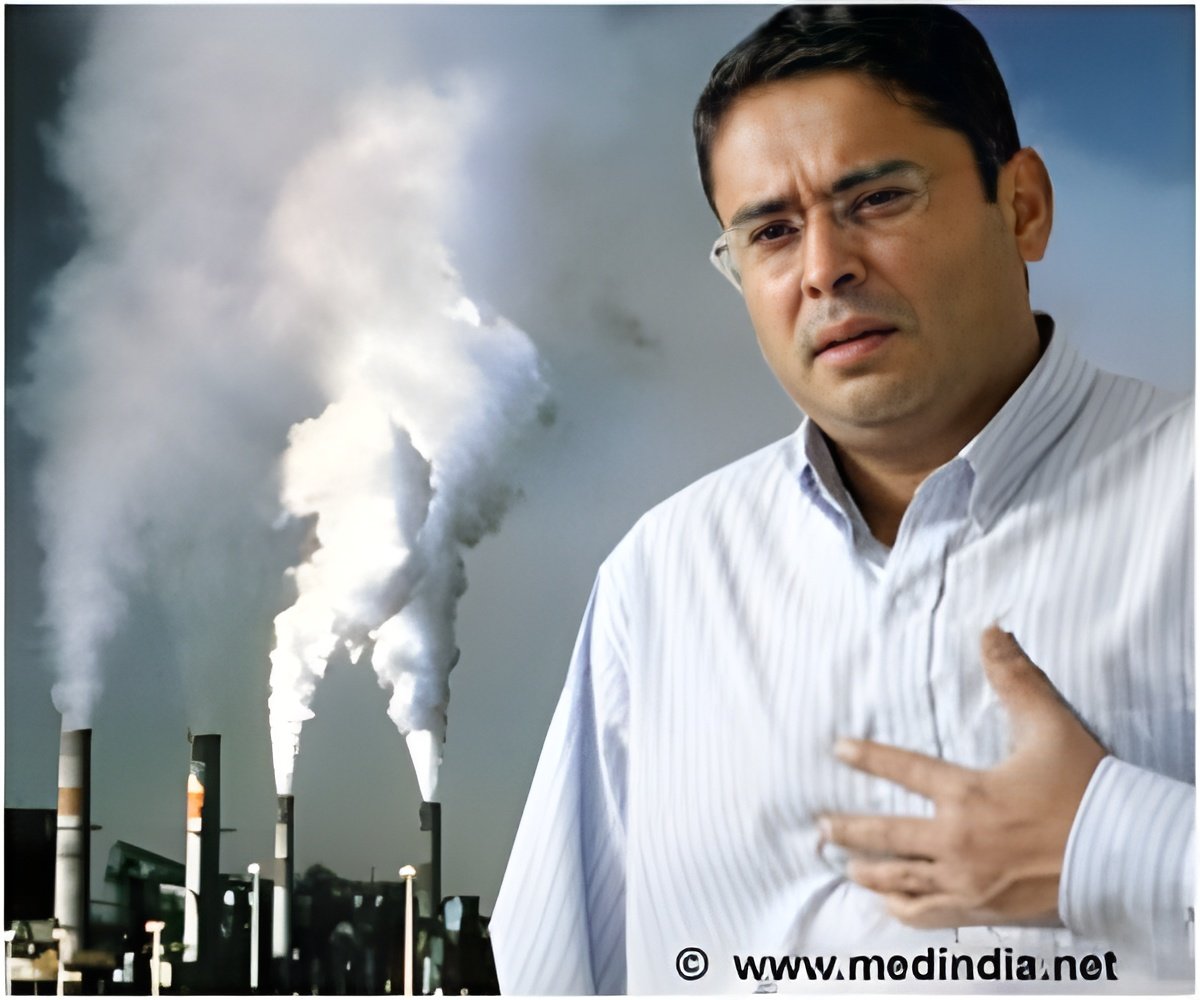
Death rate due to air pollution has increased fourfold over the last decade, with over eight million deaths worldwide, according to WHO.

"The resolution highlights the key role national health authorities need to play in raising awareness about the potential to save lives and reduce health costs, if air pollution is addressed effectively," according to a press statement from the World Health Organization (WHO).
WHO member states have been asked to develop air quality monitoring systems to improve surveillance for all air pollution related illnesses and also promote clean cooking, heating and lighting technologies and fuels.
WHO ranked Delhi as the most polluted among 1,600 cities in the world last year. According to a report by WHO, air pollution in Delhi is 10 times higher than acceptable standards.
According to WHO, exposure to air pollution leads to increased risk of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, such as strokes, ischemic heart disease and respiratory diseases.
By next year, WHO is expected to propose a roadmap for an enhanced global response by the health sector that reduces the adverse health effects of air pollution.
Advertisement