Linking rheumatic heart disease services into existing HIV/AIDS clinics and primary health care centers can reduce the death rate of RHD.
‘If medical sites are broadly available and not confined to one location, similar to the AIDS centers, patients will be more likely to comply with the demanding requirements for the treatment of rheumatic heart disease.’





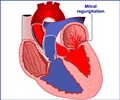
Rheumatic heart disease can result in severe heart damage, even death. While largely eliminated in developed countries, rheumatic heart disease leads to over 320,000 deaths each year in Africa, the Middle East, Central and South Asia, and the South Pacific. The borrowed tool, the HIV treatment-cascade, features a series of distinct, sequential steps for assessing supplied care. The Case Western-led team recently published a study of 1,500-plus patients in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcome describing its use in combating rheumatic heart disease, one of the earliest attempts to adapt the model for another serious illness.
A central premise of the cascade is that if medical sites are broadly available and not confined to one location, usually a big city, patients will be more likely to comply with the demanding requirements that treatment can entail, whether taking several medications daily, as with AIDS, or tolerating recurrent needle injections, as with rheumatic heart disease.
In line with this premise, a chief finding of the new study is that difficulty getting to and from care was a more significant barrier to patient progress than either obtaining prescriptions for penicillin injections or patient-adherence to the monthly shot schedule.
Of the 82 percent of patients who remained alive during the study, only 57 percent stayed in care for at least a year. But of those, more than 90 percent came for their shots at least nine months of the year.
Advertisement
"Patients in poorer nations who develop a chronic disease, whether it's AIDS, diabetes, or rheumatic heart disease, face similar obstacles to care," said the study's lead author, Chris Longenecker, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
Advertisement
The groundwork for the study was laid in 2012 when RHD Action Uganda, a collaboration of Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Children's National Medical Center (Washington, DC), and Makerere University, Uganda Heart Institute, Joint Clinical Research Center, Mbarara University of Science and Technology, and Gulu University School of Medicine -- all from Uganda -- was established with funding from the Medtronic Foundation.
The program works to expand access to rheumatic heart disease care throughout the country. Core components include integrating rheumatic heart disease services into existing HIV/AIDS clinics and primary health care centers, establishing new regional care centers (four to date), training local health workers to deliver rheumatic heart disease services, and developing a national registry, which now keeps track of over 1,800 patients.
Because the new analysis adjusted for distance to the nearest health center, improved retention at regional sites is also likely attributable to more staff, funding, and ancillary resources per capita dedicated to tracking patients -- resulting from the decision to decentralize care.
Said Longenecker, "By offering care at the HIV/AIDS clinics, and establishing new care sites, we were able to dramatically increase care options for people living with RHD throughout the country. If efforts such as ours can be expanded throughout Africa, and low-income countries elsewhere, rheumatic heart disease can become a thing of the past in those places, as it has throughout the western world."
Source-Eurekalert