- Trichomoniasis: a brief review of diagnostic methods and our experience with real-time PCR for detecting infection - (https://s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/thejournalhub/10.15570/actaapa.2015.3/actaapa.2015.3.pdf)
- Trichomoniasis - CDC Fact Sheet - (http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm)
- What is Trichomoniasis? - (http://www.std-gov.org/stds/trichomoniasis.htm)
- Trichomoniasis - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trichomoniasis/basics/definition/con-20034596)
What is Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that often causes urethral infections in men and vaginal infections in women. The incidence of trichomoniasis is higher than that of gonorrhoea or chlamydia put together.
According to estimates by WHO, 276.4 million people were infected with trichomoniasis in 2008 in the world. Around 3 to 5 million people in the US are infected with trichomoniasis. It more commonly affects older women. It is a curable infection.
What are the Causes of Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, a protozoan parasite. The parasite is usually located within the prostate or the urethra (internal area of the penis) of males or in the genital tract (vagina and vulva) of females. Humans are hosts for this parasite. In certain individuals, infection exists even if symptoms are absent. The parasite can exist in sheets, underwear, and towels and get transmitted to individuals.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Trichomoniasis?
Many people who suffer from Trichomonas do not exhibit any signs or symptoms. Some individuals start to exhibit symptoms within a span of 5 to 28 days. The symptoms may be mild itching to severe inflammation. Pregnant women who are infected with trichomoniasis are at risk of their membranes rupturing prematurely, thereby delivering children prematurely with low birth weight (< 2.5 kgs). Inflammatory disease of the pelvis is another complication of trichomoniasis.
Women who exhibit symptoms display characteristics that include irritation/burning/redness in the genital area, pain during sexual intercourse or urination, and vaginal discharge that has a bad odor (severe vaginitis). The vaginal discharge may be of different colors such as yellow, gray, white, or green. One characteristic of trichomoniasis is cervicitis or inflammation of the cervix, with small bleeds in the cervix (strawberry cervix). These features can distinguish trichomoniasis from other sexually transmitted conditions. However, it is difficult to detect. Pain in the lower abdominal area is rarely observed.

Symptoms in men include pain during ejaculation or urination, itching within the penis, and discharge from the urethra (urethritis).
How to diagnose Trichomoniasis?
Laboratory tests that detect trichomoniasis infection are explained below:
Trichomonas cultures
This is a very sensitive procedure and can provide accurate information on the presence of Trichomonas. Culture is growing bacteria from a sample in a suitable medium in a laboratory. It is a useful test if small amounts of bacteria are present which cannot be detected by microscopic examination. In order to obtain good cultures, the urethral or vaginal swabs that are collected should be introduced in the medium within 1 hour. InPouch TV® culture medium and Diamond’s medium are used for culture of Trichomonas. Cultures are examined for 5 days for the growth of Trichomonas.
Microscopy
In this diagnostic procedure, a microscope is used to analyze urethral or vaginal secretions on wet mount slides. The trichomonads can be observed under the microscope with jerky motions. Examination of specimens should be carried out within minutes of collection of the discharge. Any errors in collecting the specimens, transportation, or storage affect the viability of the specimens. The test may not be reliable in males due to lesser number of organisms.

Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT)
These tests involve the amplification of nucleic acids, which are part of the DNA or RNA of the organism in question. Samples such as vaginal swabs, urine, and endocervical swabs are appropriate to obtain nucleic acids that can be amplified by simple laboratory techniques like PCR (polymerase chain reaction). These tests can be performed with minimal quantity of samples.
Rapid diagnostic tests
In order to avoid the hassles of sample collection and specific storage conditions observed in the above techniques, a few rapid diagnostic tests have been developed. These are useful only in women with symptoms of trichomoniasis.
- Affirm VPIII®: This diagnostic test detects the presence of nucleic acids of Candida albicans, T.vaginalis, among others. It has been approved by the FDA but has not been used to detect trichomoniasis in asymptomatic men or women.
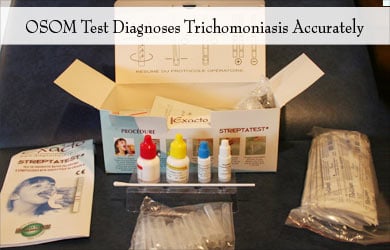
- OSOM Trichomonas rapid test (OSOM TV®): This test involves a dipstick that tests for T vaginalis. It detects Trichomonas infection in individuals with symptoms. This test is available since 2013 and has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- Tv latex® agglutination test: This test uses latex for aggregation of the Trichomonas proteins. When trichomonas is present in a sample, it causes beads coated with antibody to clump together. Although it is commercially available, it has not been approved by the FDA or in Europe.
How is Trichomoniasis treated?
Trichomoniasis can be cured with oral antibiotic drugs, such as tinidazole or Metronidazole These medications produce side effects in individuals who consume alcohol within 1-3 days of drug consumption. Therefore, patients are advised to avoid alcohol around the time they take the drug. The medications are relatively safe to be consumed by pregnant women.

Recurrence of trichomoniasis occurs in 1 in 5 people within 3 months following treatment. Hence, to avoid recurrence, it is recommended that individuals do not indulge in sex during the treatment phase and they wait for a week after the symptoms disappear.
Prevention of Trichomoniasis - Health Tips
Since Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection, it is preferable to abstain from sex if one partner suffers from the infection. In the event of sexual intercourse, it is recommended that the couple talk about the risks of infection before the act.
If an individual notices the characteristic symptoms of sexually transmitted infections, it is advisable to consult a physician to confirm the diagnosis.
Condoms are useful in preventing and controlling Trichomoniasis infections. However, even with the use of condoms, there is a chance of transmitting the infection since all infected regions are not covered with condoms.






