Researchers from Louisiana State University, New Orleans claim to have identified a key contributor in the development of Alzheimer's disease.
They revealed that a fragment of ribonucleic acid (RNA), once thought to be no more than a by-product, plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation and the development of Alzheimer's disease.The tiny piece of RNA, or microRNA, called miRNA-146a was found in increased amounts in stressed human brain cells and Alzheimer's disease
Lead researcher Walter J. Lukiw, PhD, Associate Professor of Neuroscience and Ophthalmology at LSU Health Sciences Centre showed that MiRNA-146a targets the messenger RNA of an important anti-inflammatory regulator called complement factor H (CFH).
Testing both control cells and Alzheimer's disease-affected tissues, they found that miRNA-164a appears to reduce the amount and bioavailability of CFH, promoting the inflammation of brain cells and contributing to the development of Alzheimer's disease.
"The goal of these neuroscience research studies is to further our understanding of the molecular biology and genetic mechanisms associated with Alzheimer's Disease and to advance the design of therapeutic strategies to counteract this common and tragic neurological disorder," said Dr. Lukiw.
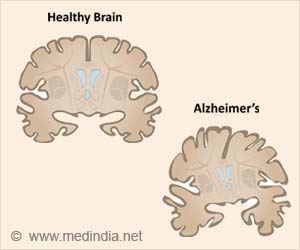
The most common form of dementia, Alzheimer's Disease is a fatal, age-related neurodegenerative disorder characterized clinically by the progressive erosion of cognition and memory.
Advertisement
Source-ANI
SRM