‘Good oral health can prevent periodontal disease and also other health related conditions associated with it including esophageal cancer.’
Tweet it Now
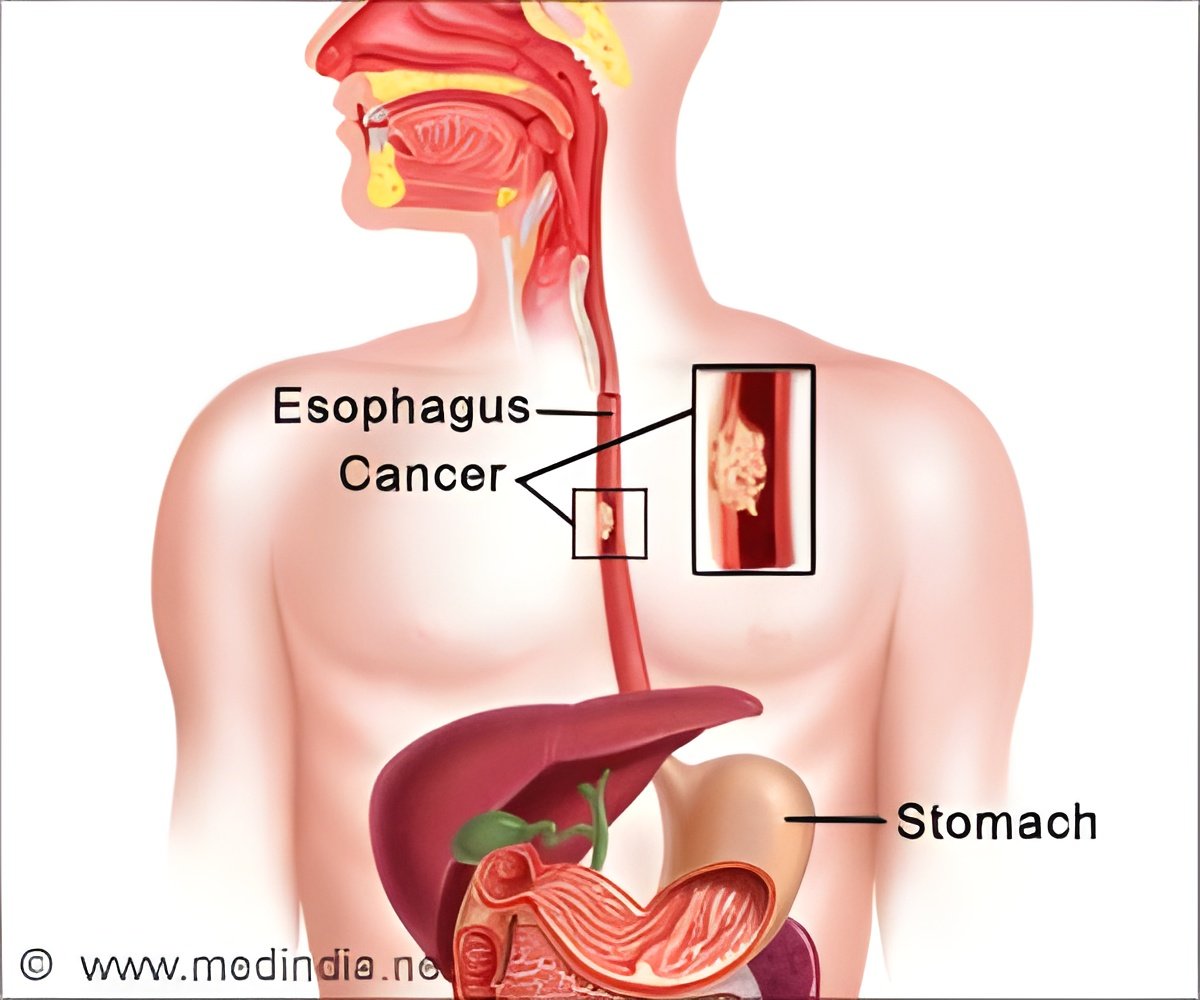
Jiyoung Ahn, PhD, an associate professor and associate director for population science at the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Center at NYU Langone Health in New York were the authors of this study.Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common cancer and the sixth leading cause of cancer death worldwide, Ahn said. Because the disease is often not discovered until it has reached an advanced stage, five-year survival rates range from about 15 to 25 percent worldwide.
"Esophageal cancer is a highly fatal cancer, and there is an urgent need for new avenues of prevention, risk stratification, and early detection," Ahn said.
Previous research has shown that periodontal disease caused by certain oral microbiota has been associated with several types of cancer, including oral and head and neck cancers. This study examined whether oral microbiota were associated with subsequent risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) or esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Ahn and colleagues collected oral wash samples from 122,000 participants in two large health studies: the National Cancer Institute Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial and the American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study II Nutrition cohort.
Advertisement
Certain bacteria types were associated with higher risk of esophageal cancer. For example, higher levels of the Tannerella forsythia bacteria were associated with a 21 percent increased risk of EAC. The bacteria Porphyromonas gingivalis was associated with a higher risk of ESCC. Both species of bacteria are linked with common gum disease, Ahn noted.
Advertisement
Ahn said the finding on Neisseria indicates that certain bacteria may have a protective effect, and future research could potentially examine whether these bacteria could play a role in preventing esophageal cancer.
"Our study indicates that learning more about the role of oral microbiota may potentially lead to strategies to prevent esophageal cancer, or at least to identify it at earlier stages," Ahn said. "The next step is to verify whether these bacteria could be used as predictive biomarkers."
Ahn added that the study confirms that good oral health, including regular tooth brushing and dental visits, is an important way to guard against periodontal disease and the growing list of health conditions associated with it.
Source-Eurekalert