- Urinary Incontinence in Older Adults - (https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/urinary-incontinence-older-adults#)
- Urinary Incontinence - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/urinaryincontinence.html)
- About Urinary incontinence - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/definition/con-20037883)
- Urinary Incontinence - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559095/)
- Overview of Overactive Bladder, Prostatitis, and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms for the Primary Care Physician - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1472848/)
- Urinary Incontinence in Neurological Disease - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK132842/)
- Urinary incontinence in multiple sclerosis: prevalence, severity and impact on patients' quality of life - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27120000/)
- Pelvic floor dysfunction - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/pelvic-floor)
- Post-prostatectomy incontinence: Etiology, evaluation, and management - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548645/)
- Diagnosis of Bladder Control Problems - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/bladder-control-problems/diagnosis)
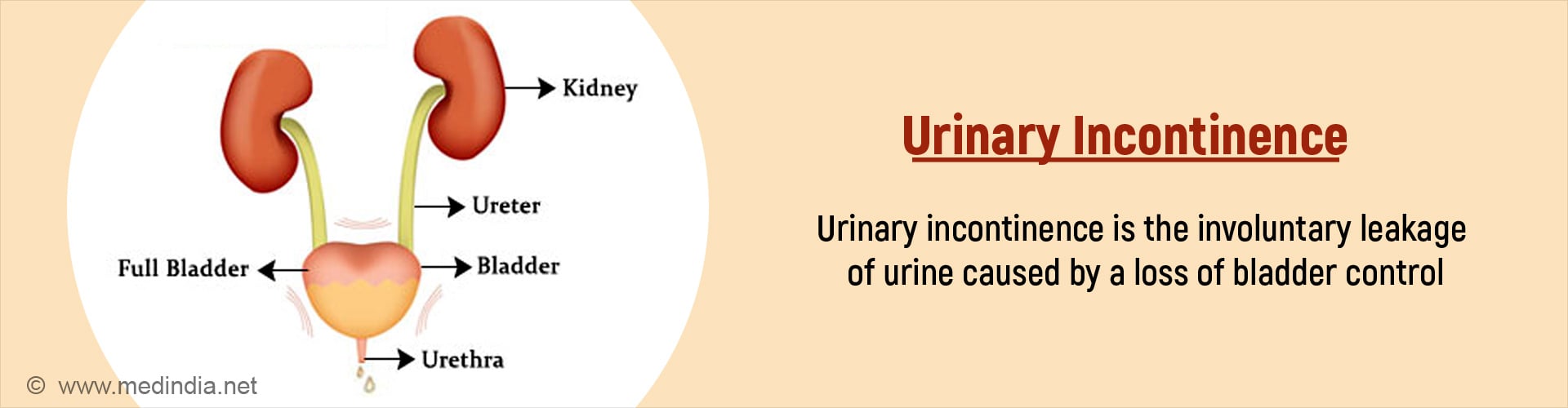
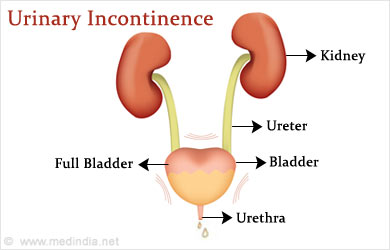
What is Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence can be temporary or persistent. It is common with aging due to weak bladder muscles. Women are more commonly affected compared to men, and this can be attributed to hormonal changes, pregnancy, childbirth, and anatomy of the urogenital tract (higher incidence of infections), among others. Obesity is another factor that increases the risk of urinary incontinence.
Temporary urinary incontinence is due to certain drinks, medications or infections. Some of the causes are:
- High caffeinated drinks
- Alcohol
- Decarbonated drinks
- Spicy/citrus food
- Artificial sweeteners
- Urinary tract infections
- Medications (blood pressure drugs, sedatives, and muscle relaxants)
Persistent urinary incontinence is caused by:
- Hormonal changes in women eg, during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause.
- Aging
- Problems with the prostate (Enlarged prostate/Prostate cancer)
- Tumors obstructing the normal flow of urine can cause overflow incontinence.
- Neurological problems like spinal injury, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, brain tumor, among others can lead to urinary incontinence by intervening with the nerve signal that acts on the bladder.
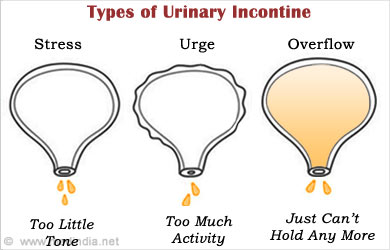
Types of urinary incontinence:
- Stress incontinence– This can happen due to stress which occurs with severe physical activity or even with cough or sneezing.
- Urge incontinence – This happens when there is a sudden urge to pass urine, but one is unable to visit the restroom in time.
- Overflow incontinence – Overflow incontinence occurs due to incomplete voiding of the bladder causing frequent or constant dribbling of urine.
- Functional incontinence – It is due to physical or psychological factors that interfere with reaching the restroom in time.
- Mixed incontinence –
This is a combination of more than one type of incontinence.
Urinary incontinence is a symptom that can be seen in various conditions like:
- Multiple sclerosis – It is an immune-related inflammatory disorder affecting the central nervous system. It commonly presents with paresthesias, muscle cramping, bladder/bowel/sexual dysfunction, optical neuritis, ataxia, tremors, dysarthria, facial twitching with weakness, heat intolerance, cognitive problems, among others. The diagnosis is based on the clinical presentation and investigations. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and spine, and lumbar puncture with Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) analysis usually help in concluding the diagnosis. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) analysis shows oligoclonal bands and intrathecal immunoglobulin G.
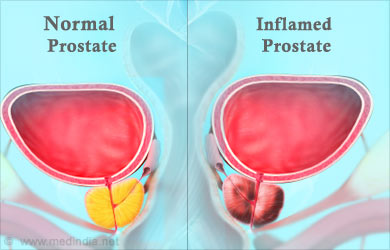
- Prostatitis – It is the inflammation of the prostate gland. Common symptoms include increased frequency, urgency, dysuria, nocturia, weak stream, incomplete voiding, fever, chills, fatigue, muscle pains, and joint pains. Urine analysis with culture, fractional urine studies with cytology, and transrectal ultrasound to check the prostate morphology are useful in making a diagnosis.
- Spinal cord neoplasms – It is the tumor (primary tumor or metastatic tumor that has spread to the spinal cord) of the spinal cord causing compression of the cord, or the nerves that arise from the spinal cord innervating various organs like bladder, bowel, among others. The presentation varies depending upon the affected nerve. Bowel dysfunction presents with urinary hesitancy, urinary incontinence or urinary retention. The diagnosis may be done with plain X – rays, MRI of the spine, nuclear scan of the spine, and by checking the post-voidal residual volume.
- Spinal epidural abscess – It is the abscess in the epidural space of the spinal cord, which causes compression of the cord due to expansion leading to sensory and motor symptoms. Common symptoms related to bladder dysfunction include urinary hesitancy, urgency, incontinence, or retention of the urine Blood investigations and MRI of the spine are helpful in forming a diagnosis.
- Uterine prolapse – It is the descent of the uterus from its normal position through the pelvis into the vagina. Common symptoms include feeling pressure in the pelvis with pain, pain during intercourse, urinary incontinence, feeling of urgency/frequency, excessive vaginal discharge, and protrusion of the tissue through the vagina. Pelvic ultrasound and blood investigations are helpful in forming a diagnosis.
- Cystitis – It is the inflammation of the bladder lining. It presents with increased urinary frequency/urgency, dysuria, urinary incontinence, suprapubic tenderness, blood in the urine, chills, fatigue, and fever. The diagnosis may be concluded with urine analysis, culture, and cystoscopy.

- Spinal cord trauma – It can result in sensory, motor, and autonomic dysfunction. The presentation varies depending on the level of the injury. The loss of bladder control can result in urinary incontinence or incomplete voiding of the bladder. Plain X-rays, MRI of the spine with measurement of the postvoidal residual volume help in forming a diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which doctor should I consult in case of Urinary incontinence?
It is best to consult a Urologist.
2. Who is at increased risk of getting urinary incontinence?
Factors like aging, obesity, diabetes, women (due to pregnancy, child birth, menopause, and female anatomy that lead to loss of strength in the pelvic muscles), and neurological disorders increase the risk of developing urinary incontinence.
3. What are the types of urinary incontinence?
Depending upon the mechanism causing urinary incontinence, there are various types. They are:
- Stress incontinence
- Urge incontinence/Overactive bladder
- Functional incontinence
- Overflow incontinence
- Mixed incontinence
- Transient incontinence
4. How is urinary incontinence diagnosed?
Urinary incontinence is diagnosed on the basis of symptoms, such as how often you are required to empty the bladder, when is it happening, and how often are you experiencing it, history of other medical conditions that you are having, medications that you are on, and related investigations. Tests like ultrasound abdomen, cystoscopy, urine analysis, and urodynamic studies are useful in concluding the cause for urinary incontinence.
5. What are the treatment options available for urinary incontinence?
Treatment may be with behavioural treatment, drugs, devices, and surgery. Certain lifestyle changes can also help cope with this situation.