- CME-Occult and Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Causes and Clinical Management: Obscure Bleeding - (https://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/718890_3)
- Medline Plus- Health topics- Gastrointestinal Bleeding - (https://medlineplus.gov/gastrointestinalbleeding.html)
- Mayo Clinic-Diseases and conditions- Gastrointestinal bleeding - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gastrointestinal- bleeding/symptoms-causes/syc-20372729)
What is Gastrointestinal Bleeding?
- Gastrointestinal bleeding (GI bleed) refers to any form of hemorrhage or blood loss that occurs in the gastrointestinal tract, which extends from the mouth to the anus. Bleeding in the digestive tract is only a symptom and it is important to find out the root cause or disease causing it.
- The upper digestive tract includes the esophagus or food pipe, the stomach and first portion of the small intestine (duodenum). The lower digestive tract comprises the remaining large portion of the small intestine, colon, rectum and anus.
- The bleeding can come from one or more of the portions of the digestive tract such as an ulcer in the stomach or inflammation of large areas of the small or large intestine.
- Bleeding can range from mild or almost undetectable to severe and life-threatening. Occasionally bleeding is detected only by laboratory tests as it is not visible to naked eye. This type of bleeding is known as “occult” or “hidden” bleeding.
What Causes Gastrointestinal Bleeding?
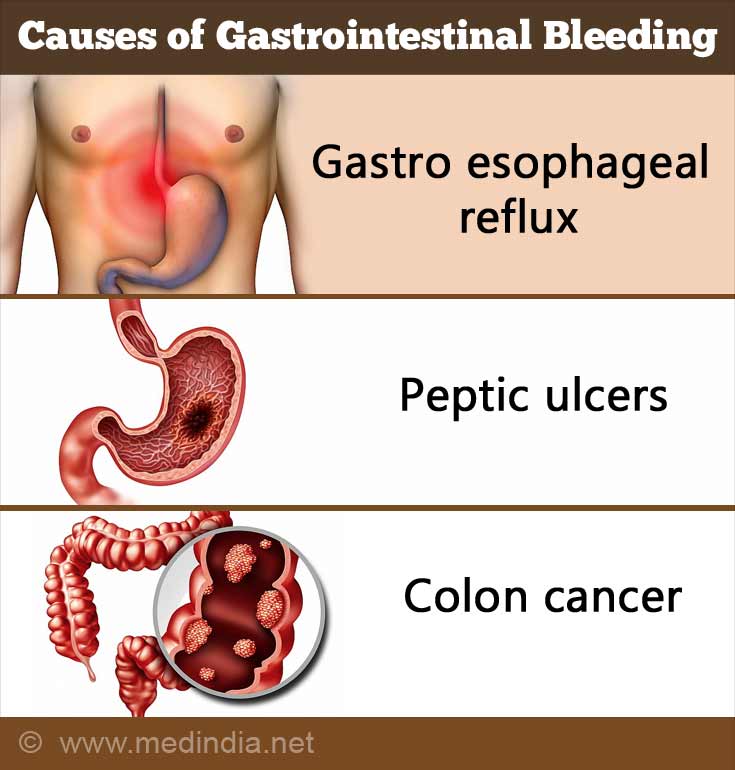
Esophagitis or inflammation of the esophagus.Gastro esophageal reflux - Stomach acid that refluxes back into the esophagus from the stomach can cause irritation and may lead to bleeding.- Gastritis (inflammation in the stomach) - This is commonly found due to excessive alcohol consumption, H-pylori infection and regular intake of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on a regular basis.
- Tears or inflammation in the esophagus - This is usually caused by severe vomiting, severe coughing, hiccups or during childbirth.
- Enlarged veins at the lower end of the esophagus or the upper stomach - These are known as varices which may break open and bleed. Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of esophageal varices.
- Peptic ulcers - The ulcer in the stomach may enlarge and erode through a blood vessel, causing bleeding. Ulcers are mainly due to medication, Helicobacter pylori infection and stress.
Cancer of the stomach , colon or esophagus.- Hemorrhoids (Piles) - These are the most common cause of hemorrhage in the lower digestive tract. Hemorrhoids are enlarged veins in the anal area that can rupture and bleed heavily.
- Fissures in the anal region - Tears in the lining of the anus can also cause bleeding and severe pain.
- Intestinal infections - Inflammation and bloody diarrhea can result from intestinal infections.
Ulcerative colitis - Inflammation and bleeding from tiny ulcerations in the colon may result in bloody stools.Crohn#$#s disease - It is an immune system condition which may cause inflammation and rectal bleeding.- Diverticular disease - These are little pouches that bulge out from the colon wall.
- Angiodysplasia (vascular malformations). This is more common in later stages of life where the blood vessels of the large intestine may cause bleeding.
- Insufficient blood supply - This results in insufficient oxygen supply and damage to the cells lining the intestine which may result in GI bleed.
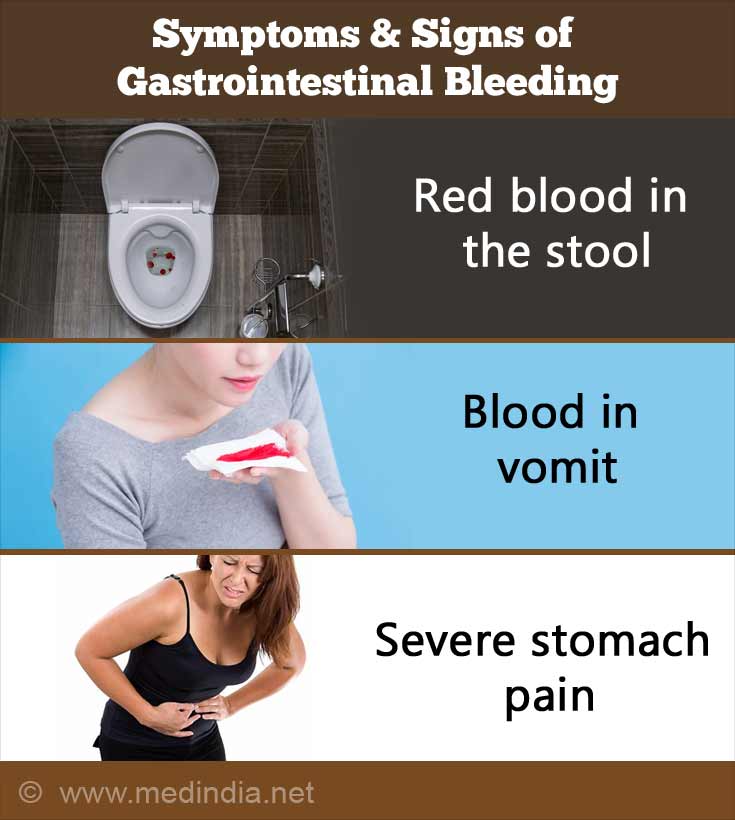
What are the Symptoms & Signs of Gastrointestinal Bleeding?
- If there is bleeding from the lower GI tract (rectum or the lower colon), bright red blood (hematochezia) will be seen in the stool. The stool may be mixed with darker blood if the bleeding is higher up in the colon or is in the small intestine.
- When bleeding occurs from the upper GI tract, the stool is usually blackish, tarry (melena) and has a very foul smell.
- In upper GI bleeding, the vomit may be bright red if active bleeding is occurring or has a "coffee-ground" appearance when the bleeding has occurred earlier or is not very heavy.
- The stool color may not change if the bleeding is slight.
- Some medications such as iron, bismuth and antibiotics such as cefdinir can give the stool a red or black appearance that looks like blood. Some vegetables such as beetroot or soft drinks such as coke, Pepsi, Thumbs up also change the color of the stools which may be mistaken for blood.
- In cases where there is sudden, massive bleeding, you may feel breathless, weakness, dizziness and have severe crampy pain and diarrhea. You could also go into shock, with drop in blood pressure and a rapid pulse.
- If bleeding is slow and happens over a long time, you may gradually feel fatigue, weakness, lethargy, shortness of breath along with pale skin and mucous membranes due to gradual anemia.