What are the Different Water Borne Diseases?
Disease which are transmitted by drinking contaminated water
| Disease | Symptoms | Transmission | Treatment |
| Bacillary Dysentery/ Shigellosis |
| Bacillary dysentery is caused by four species of the Genus Shigella
Shigella species spread by faecal-oral route |
|
| Cholera |
Sanitation, food safety and hygiene practices are inadequate. |
| |
| Hepatitis A |
|
|
|
| Typhoid fever |
|
Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi causes Typhoid and Paratyphoid fevers. |
Ciprofloxacin Co-trimoxazole |
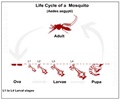
| Malaria |
|
|
|
| Disease | Symptoms | Transmission | Treatment |
| Dengue fever |
|
|
|
| Ascariasis/ Round worm Infestations | Symptoms include
|
|
|
| Campylobacteriosis |
|
|
|
| Giardiasis |
|
|
|