Treatment of Cancer of the Uterus
Treatment of uterine cancer begins within a few days after diagnosis. Usually the patient is not be in a frame of mind to concentrate on what is going on and hence it is better for them to be accompanied by a friend or a family member.
The choice of treatment depends on the age and health status of the woman and the stage and progress of the disease.
There are different choices of treatment methods available for uterine cancer. The doctor is the best person to decide on the best treatment suitable for the person. The patient could seek a second medical opinion if she so desires.
Some of the common treatment methods are described below:
- Surgery:
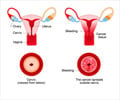
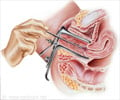
Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) is the most common treatment procedure for uterine cancer. It is usually carried out by making an incision in the abdomen. Sometimes the fallopian tubes and the ovaries on both sides are removed- this procedure is known as Total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo--oophorectomy. During surgery a part of the uterine tissue is biopsied to be examined under the microscope. This is done to confirm the diagnosis and to stage the disease. If the lymph nodes near the uterus has cancerous cells then it indicates that the disease has spread to other parts of the body and this situation may warranty other treatment options besides surgery. If the cancer is confined to the inside of the uterus then surgery may be the only treatment required.Hysterectomy can sometimes result in loss of sexual intimacy. Although the vagina is adequate to continue sexual relationship the loss of intimacy is something that maybe difficult to describe to the partner.
- Radiotherapy:
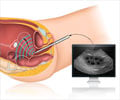
This is a localized treatment in which high-energy gamma rays are focused on the affected part to destroy cancer cells.Radiation may be the sole treatment in a few patients. However, some patients with Stage I, II, or III uterine cancer require a combination of surgery and radiation.Radiation may be given to shrink the tumor before surgery or, may be given to destroy the remaining cancer cells after surgery.Radiation therapy may be given externally or internally. In the former, radiation is provided from outside to focus on the tumor while in the latter, tiny tubes of radioactive substance are inserted through the vagina and implanted there for a period of time.It is usually advisable not to have intercourse during radiation therapy, however after a few weeks of treatment this should be possible. If vaginal dryness is experienced one should seek help from nurse or the doctor.
- Hormonal Therapy:
This involves methods by which cancer cells are deprived of hormones that they may need to grow and flourish. It is a systemic treatment and is usually meant for women in whom the cancer has advanced or metastasized.
Side effects such as pain, fatigue, nausea, inability to eat and vomiting are common in these patients who have undergone treatment. Radiation therapy may cause reddening of the skin, dryness and itching of the vagina, burning, diarrhea or loss of hair.
Hormonal therapy may lead to weight gain or menstrual irregularities.
Follow up care after treatment is absolutely vital in controlling the disease. Regular health check -ups, discussions with the doctor and following a healthy and balanced diet is important in managing the cancer.