Ultrasound / Ultrasonography Types
The use of sound waves of high frequency, to penetrate the skin and generate an electronic photographic image or video of an internal organ, is called ultrasonography or ultrasound. Only soft tissues can be penetrated by ultrasound. Bones are too dense, while lungs and the intestinal tract have air, which interferes with the sound waves. Based on the organ or condition in question, there are different types of ultrasound. There is no risk of exposure to radiation in this technique.
Types of Ultrasound
Breast Ultrasound: Sound waves are used to examine the breast. Ultrasound is recommended if there is an abnormal mammogram, or a lump is discovered in the breast. Abnormal growth can be detected and distinguished as either a cyst or solid mass. There is no radiation risk with an ultrasound, and it helps to detect cancerous or noncancerous growth.
Renal Ultrasound: The size, shape and location of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder can be assessed by an ultrasound. With the help of a transducer, high frequency sound waves are directed through the skin and allowed to target different tissues. Based on the frequency of sound waves that are reflected, one can observe an electronic image of the kidney and the associated ureters as well as bladder. Renal ultrasound can detect obstruction, tumors, cysts, fluid collection, infection, or stones in the kidney. Renal ultrasound can also evaluate a new kidney following a transplant. A transducer with a Doppler probe is used to evaluate the velocity and direction of blood flow to the kidneys. Faintness or absence of sound waves indicates obstruction to the blood flow. Renal ultrasound procedure is hampered by the presence of intestinal gas, obesity, and presence of barium from a barium procedure.
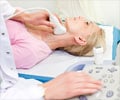
Thyroid Ultrasound: Thyroid and enlarged parathyroid glands can be analyzed with an ultrasound. As mentioned in the renal ultrasound, a transducer is passed over the neck to determine the size and shape of the glands. Any abnormal solid growth or fluid filled sacs can be determined with an ultrasound. Ultrasound can assess enlargement of the thyroid and parathyroid glands, as well as guide the positioning of a needle during a biopsy.
Abdominal Ultrasound: An abdominal ultrasound is also utilized to screen for diseases in the liver, pancreas, gall bladder, and the kidneys. It is also used to detect a bulge in the artery (abdominal aorta) that traverses the abdominal centre. This bulge is also called abdominal aortic aneurysm. Screening for an aneurysm is normally recommended for men in the age group of 65 to 75 years, and who were former or are current smokers. Women or non-smoking men are rarely screened for the aneurysm.
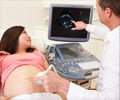
Pregnancy Ultrasound: This procedure provides information on the infant in the womb. The presence of multiple fetuses in the womb can be identified with this procedure. The efficiency of the heart and other organs of the baby can be determined. The position and size of the infant, based on the number of weeks of pregnancy, can also be determined. Ultrasound can detect the position of the uterus, and any damage to the ovaries or fallopian tubes. Patients who show abnormalities in their ultrasound are referred to appropriate specialists. An ultrasound is normally recommended between 18 to 22 weeks of pregnancy.
3-Dimnesional and 4-Dimensional Ultrasound: Variants of the regular pregnancy ultrasound, 3d and 4d ultrasound imaging techniques, provide a photographic image of the infant in the womb. The 3d ultrasound gives a 3-dimensional effect providing a photograph of the baby. The 4d ultrasound provides a moving image of the baby, like a video, where you can observe the baby smiling or yawning. An advantage of these procedures is observing any disfiguration in the infant such as a cleft-lip. However, not all clinics provide this service and it is not widely recommended due to overexposure to sound waves.