- Prevalence of Kidney Stones in the United States - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3362665/)
- Imaging Tests to Check for Kidney Stones in the Emergency Department - (https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/products/kidney-stone-imaging/consumer)
- Kidney Stone Analysis - (https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/kidney-stone-analysis/)
- Diagnostic Tests for Kidney Stones - (https://nyulangone.org/conditions/kidney-stones-in-adults/diagnosis)
- Diagnosis of Kidney Stones - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/kidney-stones/diagnosis)
What is Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are a common problem that can be seen in individuals of all age groups. In the United States, one in every eleven individuals has had a kidney stone.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Prevalence of Kidney Stones in the United States
Go to source)
Many times, small kidney stones do not cause problems and pass into the urine. They usually cause symptoms when they obstruct the flow of urine; the muscles of the urinary tract try to push the stone out, thereby resulting in colicky lower abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Some individuals may pass a small amount of blood in the urine.
The main types of kidney stones are calcium oxalate stones, uric acid stones, struvite stones and cystine stones.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Kidney Stone Analysis
Go to source)
Tests that are commonly used to diagnose kidney stones include:
Radiological tests:
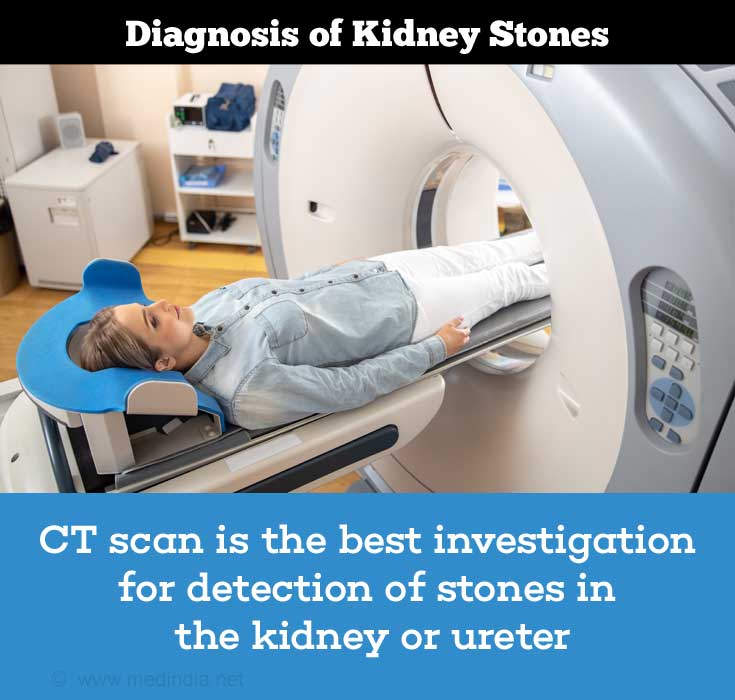
- CT scan: This is a commonly performed test for kidney stones today. A CT without contrast is a preferred test where stones that cannot be detected on x-ray like uric acid and xanthine stones can be detected. The test can also help to rule out other possible causes of the lower abdominal pain. However, the test does expose the patient to radiation.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diagnostic Tests for Kidney Stones
Go to source)
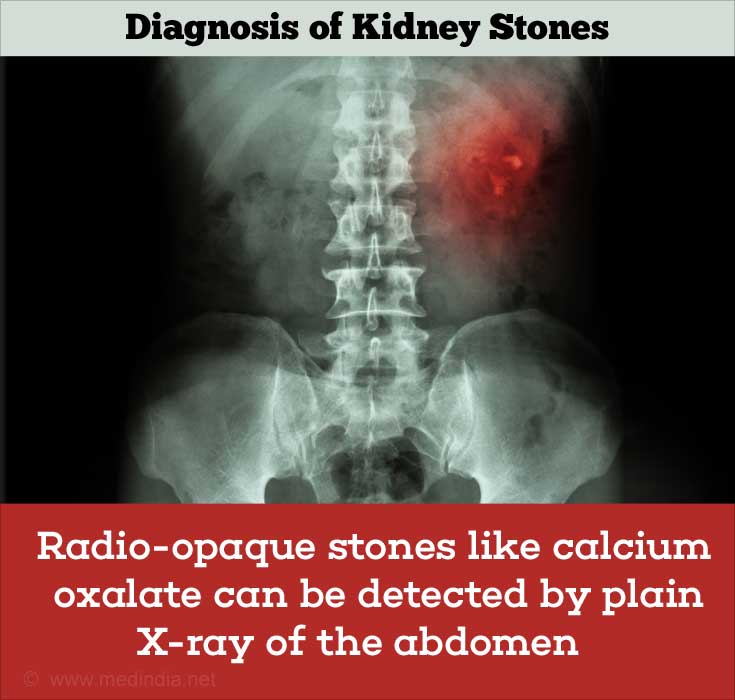
- Plain x-ray KUB: Many kidney stones especially the commonly occurring calcium oxalate stones are radiopaque and can be detected with the help of a plain x-ray used to include the kidney, ureters and bladder. Stones like pure uric acid or cystine stones may not be visible on x-ray. However, other associated changes like hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidneys due to urine build-up) may be observed in these cases, which may give a clue to the presence of a stone. Plain x-ray KUB is often used as a repeat test to study the progress of the stone through the urinary tract.
- Ultrasound: This can detect radiopaque as well as radiolucent kidney stones and can be used to study the location as well as the size of the stone. Unlike other radiological tests, it does not expose the patient to harmful radiation and is therefore a preferred option in children as well as in pregnant women.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Imaging Tests to Check for Kidney Stones in the Emergency Department
Go to source) - Intravenous pyelogram: This is a procedure where a radiopaque dye is injected into the blood. Its movement through the urinary tract is studied through serial x-rays as it is excreted from the body. A kidney stone may produce obstruction to the free flow of dye. The test also helps to establish if the kidney function is normal.
Urine examination: Examination of the urine may give clues to the presence of stones in the urinary tract. A urine examination in a patient with kidney stones may reveal the following:
- Presence of urinary crystals like calcium oxalate, uric acid and cystine which give rise to the particular type of stone
- Presence of infection that can trigger stone formation
- Presence of blood in the urine
- pH of the urine since certain stones are formed in acidic or alkaline pH(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones
Go to source)
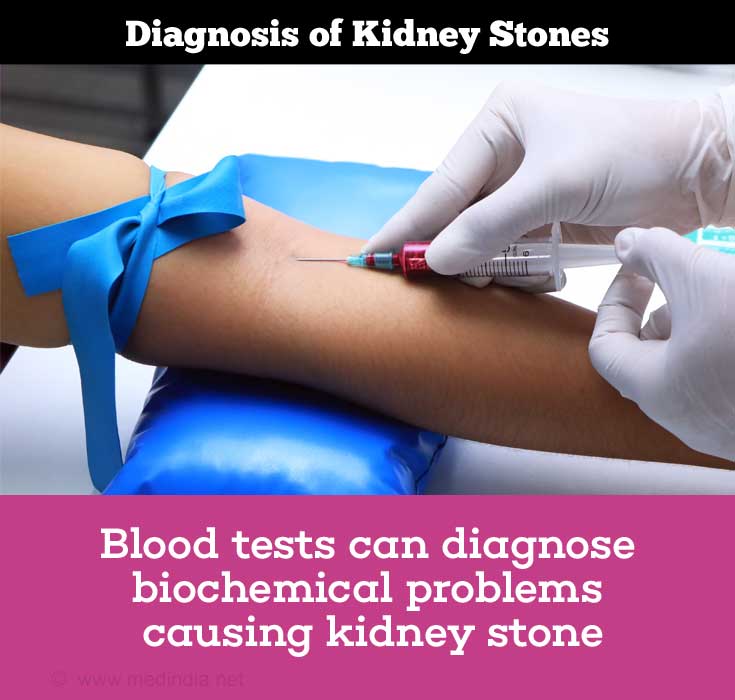
Blood tests: Blood tests may also give a clue to the presence of kidney stones. Blood tests may be used to:
- Diagnose certain biochemical problems that predispose to kidney stone formation, for example increased uric acid can cause uric acid stones, hyperparathyroidism which increases blood calcium levels can cause calcium oxalate stones.
- Test for kidney function, which may be affected due to the stone.