Symptoms, Signs & Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is predominantly a mild infection, and causes no symptoms in up to 80% of previously healthy individuals. The signs and symptoms can be discussed according to the different types of presentations:
Acute Primary Histoplasmosis
Signs and symptoms usually develop in acute infection if there is history of heavy exposure to the fungus. The symptoms include cough, fever with chills, chest pain, muscle aches and breathing difficulty on occasions. Examination may reveal signs of pneumonia. Chest X-ray may show infiltrates suggestive of pneumonia.
The other findings that may be observed include:
- Arthritis – inflammation of the joints, causing pain in the joints

- Pericarditis – inflammation of the outer layer of the heart, causing symptoms such as breathing difficulty and chest pain
- Compression of mediastinal organs and airway passages
- Bronchoesophageal fistula
Chronic Cavitary Histoplasmosis
This form of the disease is usually seen in smokers, who have pre-existing lung disease such as emphysema. It is characterized by lung lesions that are usually cavitatory and exist in the upper zones of the lung, like tuberculosis.
Symptoms include:
- Productive cough
- Shortness of breath
- Fever, night sweats, weight loss
Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis
This form is most often seen in immunocompromised individuals. The risk factors for acquiring PDH include:
- HIV/AIDS

- Extremes of age and
- Use of immunosuppressive medications.
There can be several intermediate forms of this disease, existing as a spectrum.
- The acute form can cause diffuse lung involvement, respiratory failure, shock, leading to death
- The sub-acute form causes multiple organ involvement in a slow manner. It presents with fever, weight loss and other symptoms depending on the organ involved. The usual organs involved are the liver and the spleen, but the central nervous system and adrenal glands can also be involved.
Fibrosing mediastinitis
This is a rare but serious complication of histoplasmosis. In this form, there is intense fibrosis of tissues around the lymph nodes of the mediastinum in the chest. It may cause obstruction of the airways or the blood vessels to the lung. Patients may have pneumonia, coughing up of blood or respiratory failure. Sometimes, calcified lymph nodes may erode the airways. This is called broncholithiasis.
Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Syndrome
Histoplasmosis, in its later stages may cause eye involvement, which is called Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Syndrome. The fungus may reach the eye by blood-borne dissemination from the lungs. In the eye, it causes inflammation, which eventually resolves, leaving behind scars on the retina called “histo spots”. The extent of visual loss depends on the location of these histo spots. Even though the disease is caused by Histoplasma, the fungus cannot be isolated from the affected eyes.
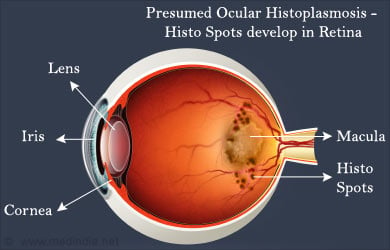
Patients are usually asymptomatic, but sometimes symptoms may develop in advanced disease. Symptoms include distorted vision and blind spots. It is diagnosed by an examination of the retina, which reveals ‘histo spots’, thinning of the retina and growth of new blood vessels in the retina.
Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis
Diagnosis of histoplasmosis is based on demonstrating the presence of the fungus in the body, either directly or indirectly. The diagnostic techniques that are of use are:
- Fungal Stain
- Sputum samples in pulmonary histiocytosis and samples from various affected organs in PDH are stained with special fungal stains and viewed under the microscope. Characteristic appearance of Histoplasma Capsulatum confirms the diagnosis
- Fungal culture
- This is the gold standard in diagnosis
- This consists of growing the organism from the sample in a compatible medium
- The disadvantages are that this method takes over 1 month to give a positive result, and sometimes the results may be negative even if the patient has the disease, because of inadequate sample
- Antigen detection
- Serologic tests for the diagnosis of Histoplasma antigen are available, and provide quick and reliable detection of the disease
- Chest X-ray
- Chest X-ray shows signs of pneumonitis
- Low exposure to the fungus may cause focal signs on the X-ray
- Heavy exposure and immune compromise may cause large signs on the X-ray
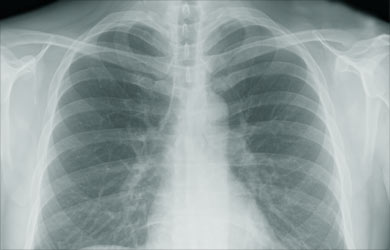
- CT
- CT chest may be used to confirm the Chest X-rays findings and to observe pleural thickening, which happens in Histoplasmosis
- CT of the abdomen can be used to visualize the involvement of intra abdominal organs
- CT of the brain is useful in CNS histoplasmosis
- Funduscopy
- Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Syndrome can be diagnosed by visualizing the retina of the eye by specialized equipment
- Examination reveals histo spots, thinning of the retina and growth of new blood vessels in the retina
- Fundus Fluorescein Angiography
- This consists of injecting a dye through a vein, which makes it possible to view the vessels in the retina more clearly