Neural Tube Defects (NTD)
Neural tube defects arise when the neural tube does not close completely by the 29th day after conception.
Neural tube defects refer to structural defects of the nervous system during the developmental process. By about the first month of fetal life, the primitive structure that gives rise to the brain and spinal cord folds upon itself to give rise to a tube-like structure, the neural tube. The upper end forms the brain and the remaining forms the spinal cord. In some cases, this closure does not occur, and gives rise to
The most common forms of NTDs are-
- Spina bifida
- Anencephaly
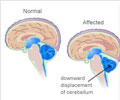
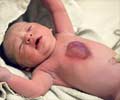
Spina bifida- When the closure defect is lower down in the neural tube, it gives rise to a condition commonly referred to as
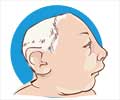
Anencephaly- When the closure failure occurs close to the upper end of the neural tube in the developing fetus, it gives rise to a condition called as ‘anencephaly’ meaning ‘no brain’. The brain and the associated structures lie exposed and highly disorganized. It usually results in a stillbirth, or death within the first few days of birth.