- Stiff Person Syndrome: A Rare Neurological Disorder, Heterogeneous in Clinical Presentation and Not Easy to Treat - (http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/278065)
What is Stiff-Person Syndrome?
Stiff-person syndrome (SPS) is a rare disease of the nervous system characterized mainly by stiffening of muscles.
It is also associated with painful muscle spasms and can result in disability.
There are several types of stiff-person syndrome:
- Classical stiff-person syndrome, which may be noted in patients with other autoimmune diseases. The trunk is usually affected first, which may later spread to the limbs and other parts of the body.
- Paraneoplastic stiff-person syndrome, which may occur in cancer patients. This type of syndrome has been noted in patients with cancer of the breast, lung, thymus or colon, or a type of cancer of immune cells called lymphoma.
- Other variants which include:
- Focal or Segmental stiff-person syndrome, which affects the limbs
- Jerky stiff-person syndrome, which causes jerking of muscles
- Progressive encephalomyelitis with rigidity and myoclonus, which progresses very fast
What are the Causes of Stiff-Person Syndrome?
The exact cause of stiff-person syndrome is not known. It is thought to be autoimmune in nature, where the body produces antibodies against its own tissues. Classic stiff-person syndrome is found in patients with other autoimmune disorders like type 1 insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (DM), Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, vitiligo or pernicious anemia. These patients have antibodies called glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies, which act against nerves that produce GABA, a chemical that relaxes muscles. This probably results in the muscle stiffness.
Patients with paraneoplastic stiff-person syndrome have amphiphysin antibodies. Amphiphysin plays a role in the transmission of nerve signals from one nerve to another.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Stiff-Person Syndrome?
Symptoms of stiff-person syndrome depend on the muscles affected. The condition is more common in women as compared to men. They include:
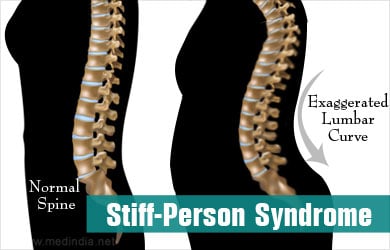
- Stiffening of the back and abdominal muscles resulting in excessive arching of the spine and postural instability
- Stiffening of the lower limbs, which occurs later and makes it difficult to walk. The patient may suffer from frequent falls resulting in fractures. Advanced cases may have joint deformities
- Stiffening of the chest muscles, making it difficult to breathe
- Stiffening of the facial muscles, which may cause difficulty in eating and speaking
- Reduction of stiffness during sleep
- Body aches due to stiffening

- Painful muscle cramps and spasms in the rigid muscles. These may occur spontaneously or in the presence of stress or stimuli like sudden noise or touch
- Psychiatric symptoms like depression, anxiety, phobias, panic disorders
How is Stiff-Person Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of stiff-person syndrome is based on history, physical examination and the following tests:
- Blood tests, which are positive for antibodies like glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies or amphiphysin antibodies
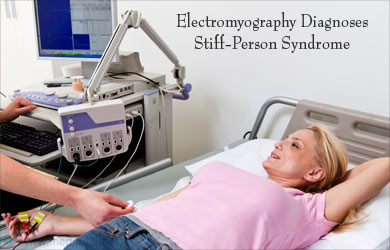
- Electromyography, which shows continuous activity in the muscles
How do you Treat Stiff-Person Syndrome?
Treatment of stiff-person syndrome includes the following:
- Drugs used to relax muscles which may include:
- Benzodiazepines like diazepam and clonazepam
- Intrathecal baclofen, where the drug baclofen is injected via a pump into the space around the spinal cord
- Antiepileptic drugs like gabapentin and tiagabine
- Botulinum toxin, which is injected into the affected muscle
- Drugs that modify the immune system which include:
- Immunoglobulin injected into the vein; the patient may get desensitized after a few treatments
- Rituximab
- Corticosteroids
- Plasma exchange: In this process, the antibodies are filtered from the plasma.
- Treatment of cancer in paraneoplastic stiff-person syndrome
- Psychotherapy and other treatments for psychiatric symptoms
- Physiotherapy for muscle stiffness
How do you Prevent Stiff-Person Syndrome?
Stiff-person syndrome cannot be prevented. However, early diagnosis can help to control symptoms with medications to some extent.
Health Tips
Patients with stiff-person syndrome get progressively disabled. Therefore, it is important to:
- Protect the patient from frequent falls, and thereby prevent injuries and fractures
- Provide physical therapy and occupational therapy so that the patient achieves some amount of independence







