Types
There are two types of Scleroderma - Localized and Systemic.
a) Localized Scleroderma
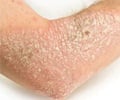
Localized scleroderma, as the term denotes, is localized to the skin on the hands and face. It is characterized by slow progression and rarely transforms to the systemic type. Localized scleroderma is further categorized into Morphea and Linear scleroderma.
Morphea Scleroderma- In this type thick, oval –shaped skin patches, with a white middle and purple border is seen, which could possibly last for several years. Eventually they reduce in occurrence and may altogether disappear.
Linear scleroderma- Here, linear bands or streaks of hard skin may appear on the face, arm or leg which is also likely to involve muscles or bones. The chances of this type of scleroderma affecting children is very low but, if it does it is likely to cause grave deformities in the arms and the legs.
b) Systemic scleroderma –Also called systemic sclerosis this disease, besides affecting the skin on the face and hands, is likely to spread to the internal organs. It must be noted that although scleroderma affects 300,000 Americans only one fifth of them have the systemic disease.
There are two types of systemic scleroderma –Limited and Diffuse – both these forms are progressive.
Limited Scleroderma is also known as CREST syndrome. CREST is an acronym of the following symptoms that appear in patients with Limited Scleroderma:-
- Calcinosis- Crystal deposits under the skin
- Reynaud’s phenomenon – Here the finger tips become very cold and blue in Color when exposed to cold. This is because of a temporary reduction in blood flow to the fingers due to narrowing of the arteries. This is often the first symptom to develop, before any of the other symptoms of CREST develop.
- Esophageal motility dysfunction occurs due to impairment of contraction of esophageal muscles effectively. This results in Gastroesophagal reflux disease (GERD).
- Sclerodactylia- Stiffness and tightening of the skin covering the fingers.
To some extent bone loss may also occur.
- Telangiectasia – A condition whereby numerous red marks develop on the face, hands and tongue. Limited scleroderma is often quite limited in its occurrence on the body and does not spread to the internal organs. It becomes a complication only if the patient develops pulmonary hypertension.
Diffuse scleroderma –This type is widespread in occurrence and can affect the skin, connective tissues and other organs. The course of the disease is often slow but it can, in some, occur suddenly and manifest as a swelling of an entire arm. If the disease is acute, it can affect internal organs and become life- threatening. Diffuse scleroderma can also occur alongside other auto- immune disordsers such as lupus and when this occurs it is referred to as mixed connective disease.