- Leone PA. Scabies and Pediculosis Pubis: An Update of Treatment Regimens and General Review. CID 2007:44 (Suppl 3): S153-S158
- Chosidow O. Scabies. N Engl J Med 2006; 354:1718-1727
- Johnston G, Sladden M. Scabies: diagnosis and treatment. BMJ 2005;331:619–22
About
Scabies is a common skin problem that affects millions of people every year the world over. It is often seen in people living in crowded and unhygienic conditions, including institutions. Children may be exposed to the infestation in schools.
Cause: Scabies is caused by a small parasite called Sarcoptes scabiei. This mite lives in burrowed tunnels in the human skin. The female lays its eggs in these burrows; the eggs hatch into larvae, which then mature on the skin surface. The entire life cycle usually lasts between 30 to 60 days.
Spread: Scabies spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact. Patients with crusted scabies have a particularly large number of mites and therefore are more contagious. Scabies could also spread via the sharing of beddings, towels, clothes and other items.
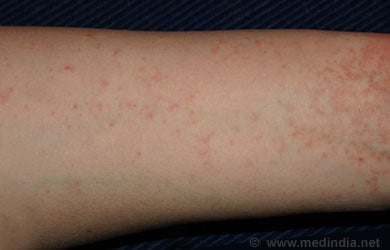
Symptoms and Signs: Symptoms and signs of scabies are:
- Scabies most commonly affects the spaces between fingers and toes, and the skin folds at the wrists, elbows, armpits, waist, feet, buttocks and ankles. In addition, scabies can also affect the area around the nipples of breasts in females, and the scrotum and penis in men. It usually does not affect the head and face, except in very small children.
- Symptoms usually develop 3 to 6 weeks after initial infestation. In case of re-infestation (infestation for a second time after complete cure), the symptoms may develop in 1 to 2 days.
- The patient complains of severe itching that worsens at night.
- On careful examination of the affected sites, burrows are visible. Other skin lesions like small swellings and crusting may also be present. Skin damage like excoriations due to itching is also obvious. Several members of the family may complain of itching.
Complications: Complications of scabies include:
- Patients with reduced immunity may suffer from crusted scabies, with severe infestation and crusts developing over the lesions.
- The skin can get secondarily infected with bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and streptococci.
- In rare cases, scabies may result in kidney disease
Diagnosis: Scabies is diagnosed based on the presence of burrows in skin folds. In addition, the mites, their eggs or feces can be detected on samples obtained from the skin under a microscope.
Treatment: Scabies treatment should not be limited to the patient alone but should cover all the members of the household. Items like bedding, towels and clothing should be washed in warm to hot water. Medications used to treat scabies are:
- Permethrine 5% cream: This cream should be applied all over the body under the face and washed off after 8 to 12 hours. It should be repeated once, a week later. Other lotions like benzyl benzoate, crotamiton and lindane are also available, but they are either less effective or more toxic as compared to permethrine.
- A steroidal cream may be applied to reduce the itching that persists despite treatment with permethrine. It should be noted that symptoms of itching and rash may persist for up to 4-6 weeks even if the scabies has been completely eliminated.
- An oral medication called ivermectin is also effective. The usual treatment is two doses of the medication given two weeks apart. A combination of ivermectin and permethrine may be used in severe cases. Ivermectin should not be given to children less than 5 years of age, and pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Antibiotics are useful to treat accompanying bacterial infection.






