- Ankylosing spondylitis - (https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/ankylosing-spondylitis)
- About Ankylosing Spondylitis - (http://www.niams.nih.gov/health_info/ankylosing_spondylitis/)
- Back Pain - (http://www.niams.nih.gov/health_info/back_pain/)
What is Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
The sacroiliac joints are joints of the lower back formed between the sacrum and the ilial bones. The sacrum is a single bone formed by the fusion of the last five vertebrae. The ilia (singular - ilium) are the largest bones of the pelvic region. The sacroiliac joint, which connects the trunk to the lower extremities, is supported by strong ligaments. There is very limited movement at the joint.
The sacroiliac joint is frequently involved in disease conditions in lower back pain. Around 15 to 30% of low back pain have been attributed to the sacroiliac joint.
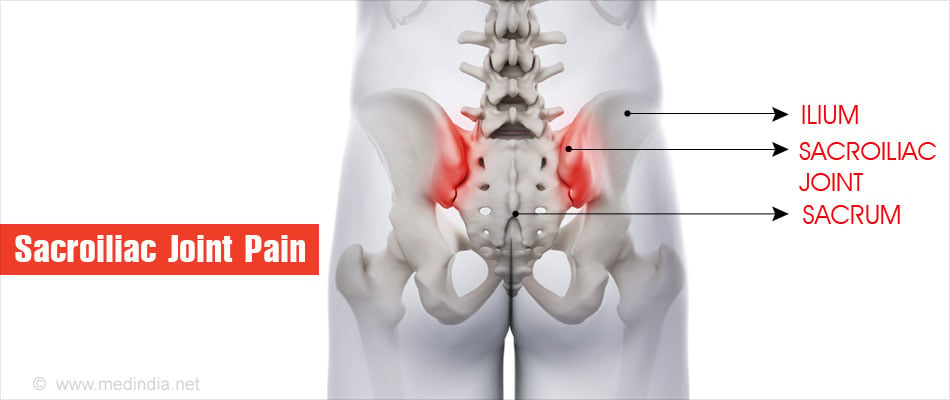
Inflammation of the sacroiliac joint is referred to as sacroiliitis. Several inflammatory conditions referred to medically as 'seronegative spondyloarthropathies' affect the sacroiliac joint. These joint diseases are referred to as seronegative since the patients’ blood samples test negative for rheumatoid factor, an antibody which is positive in patients with joint disease like rheumatoid arthritis.
What Causes Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
The sacroiliac joint may be affected by the following conditions:
- Inflammatory conditions like:
- Ankylosing Spondylitis, which affects the spine and may result in fusion of vertebrae
- Psoriasis, which is characterized by skin, joint and nail changes
- Reiter's syndrome, which causes inflammation of the joints, urethra and conjunctiva of the eye. It is more common in young males
- Septic arthritis, which is infection of the joint
- Gout, which occurs due to excess uric acid levels in the body
- Osteoarthritis, which is characterized by degenerative changes in joints

- Inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis which can also affect joints
- Trauma to the sacroiliac region like motor vehicle accidents, falling on buttocks, or repetitive lifting. The trauma could also result in a fracture involving the joint
- Tumor affecting the sacroiliac joint
What are the Risk Factors for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
Conditions that may increase the chance of developing sacroiliac joint pain or sacroiliitis include:
- Presence of HLA-B27 gene which predisposes to the development of seronegative spondyloarthropathies
- Pregnancy, which causes laxity of ligaments around the joint, excessive weight in the belly, and forward bending of the lower spine. Childbirth also increases the risk for sacroiliitis
- Altered mechanics due to different lengths of legs resulting in abnormal gait
- Prior lumbosacral spine fusion surgery, where the lower vertebrae were fused together and to the sacrum
- Spine abnormalities like scoliosis or lordosis. Scoliosis is excessive sideway bending of the spine, while lordosis is excessive forward movement of the lower spine
What are the Symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
Symptoms of sacroiliac joint dysfunction may vary according to the underlying cause. Some of the common symptoms may include:
- Pain and stiffness in the lower back
- The pain can radiate to the thigh or back of the leg
- The pain may be continuous or may appear as flare-ups with the patient normal between attacks
- Pain on one or both sides of the bottom

Additional symptoms may be noted depending on the underlying cause. For example, a patient with psoriasis may have skin lesions.
How to Diagnose Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
Diagnosis of sacroiliitis or sacroiliac joint dysfunction is based on the following:
History and Physical Examination
Sacroiliitis is diagnosed through medical history obtained from the patient, and physical examination.
Physical examination includes various tests, which provoke pain in the joint and differentiate pain arising from the sacroiliac joint from other causes of low back pain like prolapsed disc. Some of the provocative tests include:
- Flexion abduction external rotation test
- Distraction / compression provocation test
- Thigh thrust provocation test
- Gaenslen's test
- Sacral thrust test
- Focal sacroiliac joint tenderness
- Gillet’s test
A combination of tests may be more accurate in diagnosing the condition:
- Injection of Anesthetic: Injection of anesthetic into the joint temporarily relieves the pain. This helps to differentiate pain arising from within the joint and that arising from ligament strains and other structures around the joint
- Imaging Tests like X-ray, CT scan and MRI: Imaging tests help to diagnose pathologies like fracture, tumor, or osteoarthritis of the sacroiliac joint. MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) or CT scan (computed tomography scan) helps to detect changes associated with sacroiliitis earlier as compared to x-ray. Injection of a dye into the joint and obtaining subsequent images will also help to detect any pathology within the joint

- Blood Test: Blood test for HLA B27 gene can detect predisposition for inflammatory joint diseases.
How is Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction Treated?
Problems at the sacroiliac joint are usually treated conservatively.
- The patient is advised rest and asked avoid activities that can cause pain. A proper posture should be maintained at all times.
- Application of heat or ice to the joint may provide pain relief
- Physiotherapy helps to strengthen the back
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents are given to reduce pain and inflammation. Narcotic painkillers like tramadol may be used for moderate-to-severe pain over a small duration
- Muscle relaxants may also provide relief
- Alternative treatment modalities like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, ultrasound, acupuncture and cryotherapy may provide some benefit. Radiofrequency neurotomy may also be done, where the nerve that carries pain signals to the brain from the joint is destroyed
- Inflammatory conditions causing sacroiliitis may be treated with injection into the corticosteroid into the joint, disease modifying drugs sulfasalazine and methotrexate, and biological agents adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and infliximab
- A sacroiliac joint belt may provide support to the lower back

Surgery is rarely used as the last option, where the joint is fused together to negate any movement at the joint.
How Can Sacroiliac Dysfunction be Prevented?
Sacroiliitis or sacroiliac dysfunction can be prevented to some extent through the following measures:
- Exercises for strengthening the back
- Correction of any spine or lower limb deformity, either through surgery or with the use of orthotics
- Maintaining of proper posture is necessary