RTA Type 4
Type 4 RTA occurs due to decrease in aldosterone level or failure of the kidney to respond to aldosterone, hyperkalemia, spironolactone, ACE inhibitors, ARB blockers, trimethoprim, pentamidine, heparin, NSAIDs
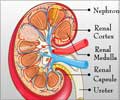
- The adrenal glands release aldosterone that acts on the latter part of the tubule. It brings about reabsorption of sodium and removes potassium and hydrogen from the blood. If the tubules do not respond to aldosterone, the hydrogen remains in the blood leading to acidosis. At the same time, the tubules cannot remove potassium. Thus, the potassium level in the blood rises causing hyperkalemia.
- Type 4 RTA could occur due to genetic disease. Other conditions like diabetes, HIV, lupus and amyloidosis with kidney damage could also cause this condition. The condition may be uncovered during intake of certain drugs like spironolactone, ACE inhibitors, ARB blockers, trimethoprim, pentamidine, heparin, NSAIDs and some drugs that suppress immunity.
- High potassium levels may cause abnormalities in heart rhythm and paralysis
- The patients usually do not develop kidney stones
- The patient should stop taking drugs that increase potassium level. Treatment includes drugs that reduce potassium in the blood like furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Alkalis are used to treat the acidosis. Fludrocortisone, an aldosterone analogue and sodium polystyrene sulfonate that helps to remove potassium through the feces may also be used.