- Periodontal health - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29926938/)
- Primary prevention of periodontitis: managing gingivitis - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25639826/)
- Risk Factors of Periodontal Disease: Review of the Literature - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4055151/)
- Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Setting Standards for Use in General Practice - (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40496-022-00323-y)
- Point-of-Care Periodontitis Testing: Biomarkers, Current Technologies, and Perspectives - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30041883/)
- Treatment of plaque-induced gingivitis, chronic periodontitis, and other clinical conditions - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11811516/)
- Systemic antibiotics in the treatment of aggressive periodontitis. A systematic review and a Bayesian Network meta-analysis - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26087839/)
About
Periodontitis, also known as pyorrhea or periodontal gingivitis, is an infection that causes inflammation of the periodontium. Periodontium refers to the specialized tissues that surround and support the teeth connecting them to the jaws.
Untreated periodontitis causes progressive loss of alveolar bone leading to loosening and eventually loss of teeth. Periodontitis, in contrast to gingivitis. is a destructive periodontal disease since the damage caused by the former is irreversible(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Periodontal health
Go to source).
The bacteria in the mouth, along with mucus and other particles, constantly produce a sticky, "plaque" on teeth. Effective brushing and flossing helps in getting rid of the "plaque". However, improper brushing and poor oral hygiene can cause accumulation of plaque that can eventually harden and form "tartar". The bacteria in tartar produce toxins to cause inflammation of the gums, called gingivitis.
The bones and connective tissues(ligaments) that support teeth break down and get destroyed due to our body's natural immune response to fight these infectious bacterial toxins. This causes loosening of the teeth and eventually needs to be removed.
Periodontitis is classified in 7 categories as follows:
- Gingivitis
- Chronic periodontitis
- Aggressive periodontitis
- Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease
- Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis/periodontitis
- Abscesses of the periodontium
- Combined periodontic-endodontic lesions
The categories 2-7 necessitate a dentist’s intervention.
Causes of Periodontitis
Poor oral hygiene, or an untreated infection of the gums (gingivitis), progresses to periodontitis. Nonetheless, poor oral hygiene is the key cause of gingivitis subsequently leading to more aggressive periodontitis.
The bacteria in the mouth, along with mucus and other particles, constantly produce a sticky, "plaque" on teeth. Effective brushing and flossing must help in getting rid of the "plaque". However, improper brushing and poor oral hygiene can cause accumulation of plaque that can eventually harden and form "tartar". The bacteria in tartar produce toxins to cause inflammation of the gums, called gingivitis.
Periodontitis follows untreated or delayed treatment of gingivitis(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Primary prevention of periodontitis: managing gingivitis
Go to source).
Risk Factors of Periodontitis
Improper oral hygiene, gingivitis, smoking and genetic susceptibility are major risk factors for chronic periodontitis.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Improper or no brushing are the key factors for the accumulation of plaque and formation of tartar, leading to infection of gums.
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis progresses to periodontitis in most cases.
- Smoking and tobacco use: Smoking is amongst the most important risk factors linked to the progression of chronic gum disease. Also, smoking can interfere with the treatment and lowers the chances of treatment success.
- Hormonal changes in women: Variations in hormones in pregnancy and
menopause can make gums sensitive. - Diabetes: Patients with
diabetes are prone to contracting infections including gingivitis. - Other illnesses and weakened immunity: Immunosuppressants prescribed in organ transplantation and the treatment of other chronic diseases like cancer or
AIDS that have an impact on immunity, can also affect the gums negatively. - Medications: Several prescription and over-the-counter medications can reduce the secretion of saliva. This can increase the susceptibility to oral infections including gingivitis and other gum diseases. Also, certain steroid-based medications lead to overgrowth of gums making it difficult to maintain oral hygiene.
- Genetic susceptibility / Hereditary factors: People with certain genotypes are more vulnerable to gum disease than others.
- Ill-fitting dentures: An ill-fitting partial/complete denture can act as a nidus for germ build-up making the oral cavity more prone to progressive gum diseases(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Risk Factors of Periodontal Disease: Review of the Literature
Go to source).
Symptoms of Periodontitis
The key symptoms for periodontitis are bad breath and soft, shiny gums that bleed easily. The description of symptoms by the patient, along with examination of oral cavity aids in diagnosing periodontitis(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Setting Standards for Use in General Practice
Go to source).
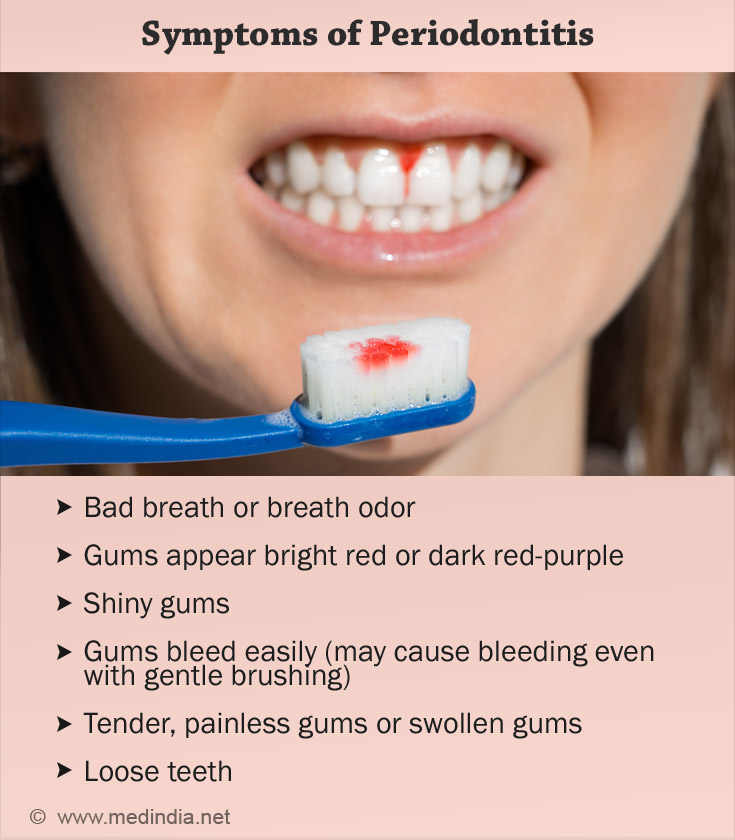
Symptoms of periodontitis include:
Bad breath or breath odor- Gums appear bright red or dark red-purple
- Shiny gums
- Gums bleed easily (may cause bleeding even with gentle brushing)
- Tender, painless gums or
swollen gums Loose teeth
Diagnosis of Periodontitis
Primarily, diagnosis of periodontitis is based on the symptoms of the patient and examination of oral cavity for plaque, tartar or
Point-of-Care Periodontitis Testing: Biomarkers, Current Technologies, and Perspectives
Go to source).
Treatment of Periodontitis
The treatment of periodontitis depends upon the stage and severity of the disease which is performed by a
Non-surgical treatments
Early grade periodontitis is treated with medications and less invasive procedures that include:
- Scaling:
Scaling is performed through instruments and ultrasonic devices to remove the tartar and bacteria from the surface of the teeth and underneath the gums. - Root planing: Root planing will make the root surfaces smooth, which prevent further buildup of tartar.
Antibiotics : Antimicrobial mouth-rinses form the first-line therapy for treating gingivitis andgum infections . Chlorhexidine is the most commonly used mouth wash. Oral or topical antibiotic gels or antibiotic microspheres containing doxycycline or minocycline are also prescribed to control bacterial growth and spread of infection.
Surgical treatments
Surgical options are recommended for advanced level or rapidly progressing periodontitis, when the non-surgical treatment and antibiotics turn ineffective. The following dental surgical treatments are used in the treatment of advanced periodontitis:
- Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery): Flap surgery involves removing a section of the gum tissue to effectively clean and remove tartar and then stitching back the removed gum tissue in its place to allow stiffer binding. Since periodontitis frequently causes bone loss, the bone is reshaped before the gum tissue is sutured back in place.
- Soft tissue grafts: The gum-line usually recedes as a result of periodontal disease, making teeth appear longer than normal. For treating this defect, some tissue is harvested from the roof of the patient’s mouth (palate) or another donor source and is reattached to the affected area. This procedure helps in treating gum recession, cover exposed roots and gives teeth a cosmetically pleasing appearance.
- Bone grafting: When the bone and tissues surrounding the tooth, root are destroyed to periodontitis, bone-grafting procedure is performed. The bone-graft is composed of small fragments of bone-tissues that may be of your own, synthetic or borrowed tissue. The bone-graft or bone-transplant prevents tooth loss, and also helps in re-growth of natural bone. Guided Tissue Regeneration Technique is used for Bone-grafting.
- Guided tissue regeneration: The procedure is used in advanced periodontitis. It allows the re-growth of the bone damaged by bacterial infection. In this procedure, the dentist places a special biocompatible material between the bone and the tooth to prevent further infection and allows effective healing.
- Enamel matrix derivative application: This technique involves deep application of specialized gels embedded with the proteins necessary for bone growth on to a diseased tooth root to stimulate healing by bone re-growth.
The success of any surgical treatment depends on several factors such as the depth of the disease, patients’ lifestyle and oral hygiene, other risk factors such as smoking or genetic susceptibility and others(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Treatment of plaque-induced gingivitis, chronic periodontitis, and other clinical conditions
Go to source, 7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Systemic antibiotics in the treatment of aggressive periodontitis. A systematic review and a Bayesian Network meta-analysis
Go to source).
Periodontitis Treatment at Home
- Brushing teeth twice every daywith a soft toothbrush using fluoride toothpaste
- Using dental floss or interdental brush for cleaning areas between teeth
- Making lifestyle changes like cessation of smoking, reducing intake of alcohol, stress and drinking water

- Controlling diabetes
- Incorporate fresh fruits and vegetables in diet
- Restrict sugary drinks and snacks