Diagnosis
The cause of menorrhagia is diagnosed using blood tests and procedures such as ultrasonography, hysteroscopy and dilatation and curettage.
Tests that are useful to detect the cause of menorrhagia include:
Blood tests
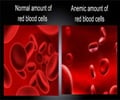
A complete blood count should be done to detect if the patient has anemia, infection or less platelets. The patient’s ferritin level as well as level of clotting factors may also need to be assessed. Thyroid, liver and kidney function tests as well as estimation of prolactin levels may be needed to rule out to rule out associated diseases.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound of the uterus may be done to detect any abnormalities such as a fibroid that may cause distortion or enlargement of the uterus. The ultrasound probe may be inserted through the vagina in a procedure called transvaginal ultrasonography. A biopsy may be taken to check for abnormalities in the inner lining of the uterus including cancer. In saline infusion sonohysteroscopy, saline is introduced into the uterus and ultrasound images are obtained. This procedure is considered superior to plain ultrasound in diagnosing abnormalities in the uterus.
Hysteroscopy
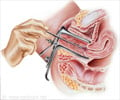
Hysteroscopy is a procedure where the inner lining of the uterus can be directly visualized by using an instrument called a hysteroscope inserted through the vagina. Uterine lesions like fibroids and polyps can be visualized and removed with this procedure. Biopsy can also be obtained.
Dilatation and Curettage
The gynecologist may dilate the cervix and take a small sample of the inner lining of the uterus. This sample is then subjected to further testing to detect any abnormality.