- Lassa fever - (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs179/en/)
- Lassa fever: origins, reservoirs, transmission and guidelines - (https://www.gov.uk/lassa-fever-origins-reservoirs-transmission-and-guidelines#treatment)
- About Lassa Fever - (http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/lassa/index.html)
What is Lassa Fever?
The fever lasts for about 1-4 weeks. The virus typically occurs in West Africa. The virus is a member of virus family Arenaviridae which is single-stranded RNA virus and is zoonotic or animal borne.
The clinical course of the disease is variable as detection of disease in affected patients has been difficult. About 80% of people who become infected with this virus have no symptoms. Around 1 in 5 infections turn out in severe disease, where vital organs such as liver, kidney and spleen are affected.
What are the Causes of Lassa Fever?
The host for the Lassa virus is a rodent known as “multimammate rat” (Mastomys natalensis). Once infected, this rodent excretes virus in urine for a long time period, may be for its lifetime. The Lassa virus is transmitted to humans through contact with food or household items which are contaminated with rodent's urine or feces. Inhaling tiny particles in the air contaminated with infected rodent excretion can also lead to infections. This kind of aerosol or airborne transmission is common in cleaning activities such as sweeping.

The virus can also be transmitted by person-to-person infections after exposure to virus in blood, tissue, secretions, or excretion of Lassa virus-infected individual. Nosocomial transmission is also possible when personal protective equipment (PPE) is unavailable or not used. Contaminated medical equipment such as reused needles is also one of the causes for infection transmission. Laboratory transmission, especially in hospitals that lack adequate infection prevention and control measures is another common cause.
People in rural areas are at greatest risk as these communities lack proper sanitation and are often crowded. Healthcare workers are also at risk if proper nursing and infection control practices are not observed.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Lassa Fever?
Approximately 80% of the symptoms are mild and undiagnosed. The onset of the disease when symptomatic is usually gradual that includes slight fever, general malaise and weakness. In 20% of infected cases, the disease progresses to more serious symptom which includes hemorrhaging (in gums, eyes, or nose), respiratory distress, vomiting, cough, swelling in face, pain in chest, back and abdomen, muscle pain, and diarrhea. Shock, seizure, hearing loss, tremors, encephalitis, disorientation and coma may be seen in late stages. About 25% patients who survive become deaf after the disease. In half of these cases, hearing partially returns after 1-3 months, whereas in some cases there is permanent hearing loss. There may be transient hair loss and gait disturbance during recovery. Of the total number of patients who are hospitalized for Lassa fever, approximately 15-20% die from the illness. However, only 1% of infections result in death. Death rates are usually high for pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy with maternal/fetal losses greater than 80%.

As the symptoms of Lassa fever are varied and nonspecific, clinical diagnosis is not easy. During occasional epidemics, fatality rate is almost 50% in hospitalized patients.
How to Diagnose Lassa Fever?
Lassa fever is difficult to distinguish from Ebola virus disease and other fever causing diseases such as malaria, shigellosis, typhoid and yellow fever.
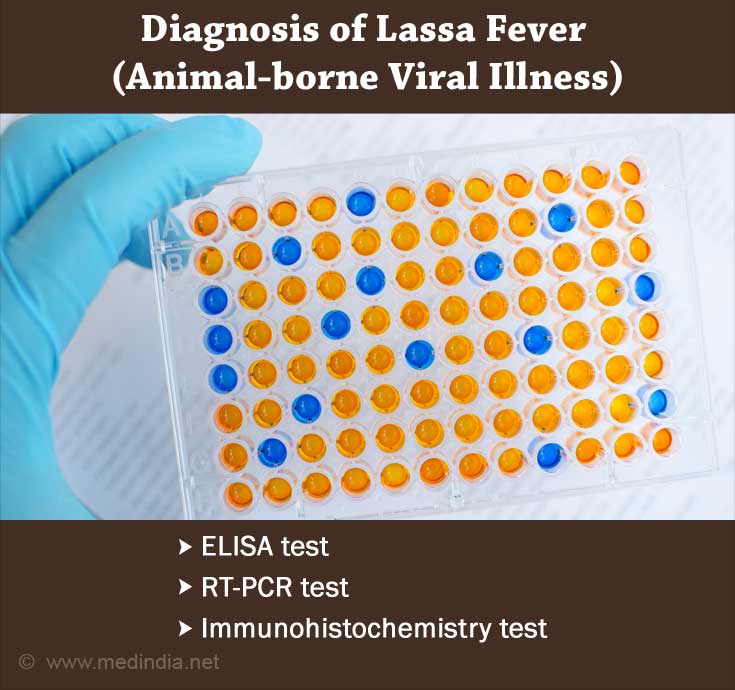
Lassa fever is often diagnosed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent serologic assays (ELISA) that detects IgM and IgG antibodies as well as the Lassa antigen. In the early stage, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) can be used. Cell culturing of virus requires 7-10 days and this procedure needs to be done in high containment laboratory with good laboratory practices. For postmortem diagnosis, immunohistochemistry test is done on formalin-fixed tissue specimens.
What is the Treatment for Lassa Fever?
Patients affected by Lassa fever, should also receive supportive care in form of maintenance of appropriate fluid and electrolyte balance, oxygenation and blood pressure and any other treatments as required.
Health Tips
- Maintaining good community hygiene and discouraging rodents from entering homes and their contact especially in geographic areas where outbreaks occur.
- Storing grains and other food stuffs in rodent-proof containers and keeping homes clean.
- Disposing garbage away from homes.
- Avoiding contact with blood and body fluids while caring for sick persons.
- In healthcare settings, staff should apply standard infection control and prevention measures when caring for patients, in spite of their presumed diagnosis. Measures include hygiene with regards to hand wash, respiration, use of personal protective equipment, safe injection and burial practices.
- Healthcare workers in close contact with Lassa fever patients should wear face protection (a face shield or a medical mask and goggles), clean non-sterile long-sleeved gown and sterile gloves for some procedures.
- Isolate the infected patients from uninfected ones till the disease has run its course.
- Patient samples must be safely handled by trained laboratory staff.
- Healthcare workers handling suspected patients for Lassa fever should immediately contact local and national experts for advice.
- Educate the people in high risk areas on ways to reduce rodent population in their homes for control and prevention of Lassa fever.