- Cecil Medicine, 23rd Ed.
- Heath DD. Immunology of echinococcus infections. In: Thompson R, Lymbery AJ, eds. Echinococcus and Hydatid disease. Wallingford, Oxon: CAB International; 1995:183-200.
About
Ever since Hippocrates described Hydatid disease, physicians all over the world have encountered it in various organs. Hydatid disease is also referred to as echinococcosis or echinococcal disease. It results from an infection due to a tapeworm of genus Echinococcus. Human echinococcosis is a zoonotic infection (i.e it is a disease of animal kingdom that sometimes can be transmitted to humans). This microscopic tapeworm is found in foxes, dogs and cats. Human cases are rare. The disease may produce cysts in the liver, lungs, brain and other organs (liver being the most common followed by lung). The incidence is greater in sheep-raising countries like Australia, Brazil, South Africa and Panama. It is common all over India, especially in Kashmir.
Any race can be affected and it is common in both men and women. Symptoms depend on the affected organ-for example liver cysts cause jaundice, abdominal discomfort while lung cysts cause cough, chest pain and hemoptysis (coughing up blood). Rupture of cysts may cause fever, urticaria, and serious anaphylactic reactions.
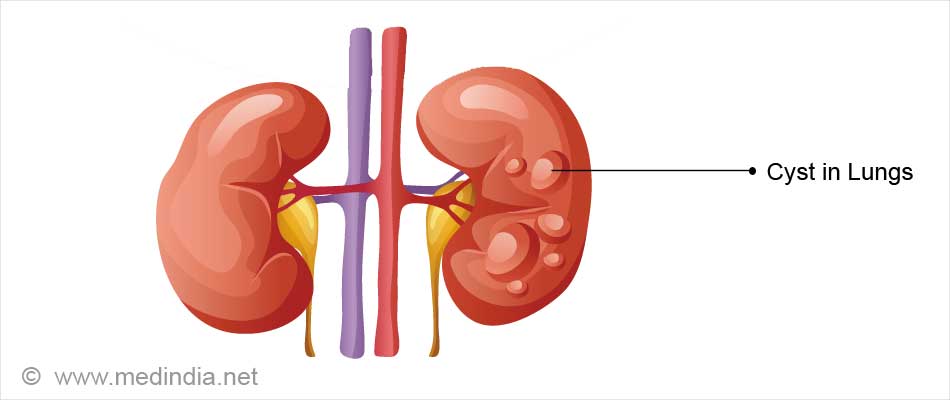
Diagnosis is done using imaging techniques, examination of the cyst fluid and serological tests.
Treatment may be with drugs like albendazole, surgery, cyst aspiration or instillation of scolicidal agents.