How can we Diagnose Cervical Spondylosis?
A physical examination may reveal that the affected person has trouble moving head toward the shoulder and rotating the head.
The doctor makes use of the neck compression test (Spurling’s Test) to confirm the presence of cervical spondylosis. The patient is asked to sit on a chair, and the doctor asks the patient to bend the head forward and to the sides while putting slight downward pressure on the top of the head. Increased pain or numbness during this test is a sign that there is pressure on a nerve in your spine. Weakness or loss of sensation is sign of damage to certain nerve roots or to the spinal cord.
The reflexes are often reduced.
Diagnostic tests
A spine or neck x-ray may be done to look for arthritis or other changes in the spine. If cervical spondylosis is present, the following changes can be seen in the X-ray-
- Bony outgrowths at the margin of the joints.
- Reduced space between the vertebrae of neck.
- The opening between the bones will be narrowed.
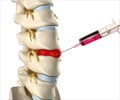
Myelography is an x-ray study which involves injecting dye or contrast material into the spinal canal. It allows careful evaluation of the spinal canal and nerve roots.
MRI of the neck is done in cases of severe neck or arm pain that does not get better with treatment, and when there is weakness or numbness in the arms or hands. The MRI features of a cervical spondylosis are as follows-
- Loss of normal curvature of neck.
- Vertebral bone canal diameter is decreased.
- Spinal canal is narrowed.
Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction velocity test may be done to examine nerve root function.