- Varicose Veins: Diagnosis and Treatment - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31150188/#)
- Hemorrhoids: From basic pathophysiology to clinical management - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3342598/)
- Varicose Veins - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470194/)
- Varicose Veins - (https://medlineplus.gov/varicoseveins.html)
- Three-dimensional CT Venography: A Diagnostic Modality for the Preoperative Assessment of Patients with Varicose Veins - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3595794/)
- Management of varicose veins - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19069022/)
- Injection sclerotherapy for varicose veins - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34883526/)
- The management of varicose veins - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4301287/)
- Diets for constipation - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4291444/)
Introduction
Varicose veins are a common condition that affects the veins, usually in the legs, causing them to become enlarged, twisted, and bulging. They occur when the valves within the veins fail to function properly, leading to blood pooling and increased pressure within the affected veins. The exact pathophysiology is debated, but it involves a genetic predisposition, incompetent valves, weakened vascular walls, and increased intravenous pressure(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins: Diagnosis and Treatment
Go to source).
While varicose veins are often considered a cosmetic concern, they can also cause discomfort, pain, and other complications. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to manage and treat varicose veins effectively.
So What Happens in Varicose Veins?
Normally the veins are stretched or pulled tight. However, if the blood flow is too sluggish, the veins slowly get dilated and twisted in order to accommodate more blood in the lumen. Another possible reason is that the valves in the veins do not function properly and the blood leaks down with gravity and gets collected in the veins of the legs. The cause of piles (or hemorrhoids) around the anus is also due to varicosity of veins around the anus(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hemorrhoids: From basic pathophysiology to clinical management
Go to source).
Are You Prone to Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins can be inherited and if there is a strong predisposition in your family, this may be the most influential risk of all. It is believed that up to 15% of adults in the western world are affected by this condition. Early stages of venous reflux may occur in as many as 25% of women and 15% of men. Later stages of venous reflux, such as venous ulceration, may occur in 5% of the population (Rabe 2016).
Varicose veins are seen globally and influenced by activity and lifestyle and are more likely to occur in women than in men(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins
Go to source).
What are the Causes of Varicose Veins?
Valves prevent the backflow of blood within the vein and keeps blood in the vein moving towards the heart. When a person with poorly functioning or defective valves stands up for prolonged durations, the blood flow actually reverses and flows down the superficial veins, when it should be flowing up towards the heart(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins
Go to source).
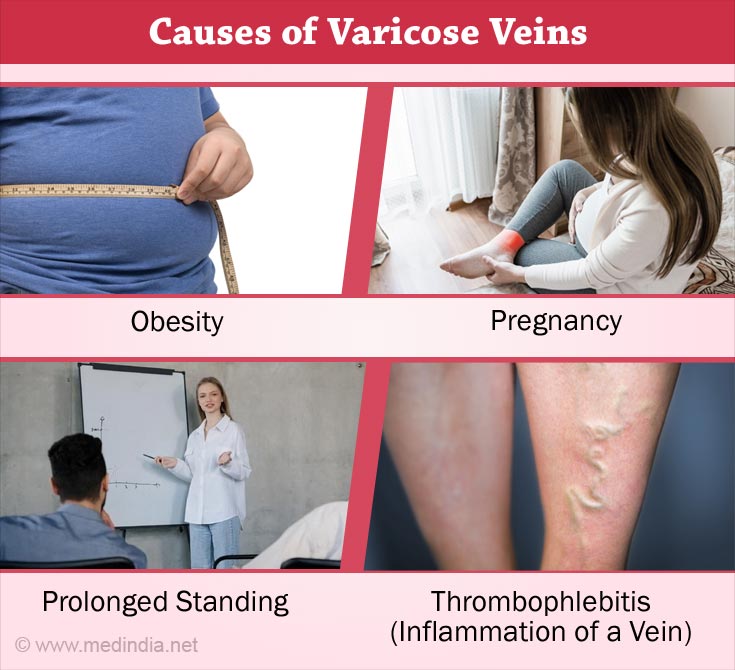
Causes and risk factors for varicose veins include -(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins: Diagnosis and Treatment
Go to source)
Age and Genetics
As we age, the natural wear and tear on vein valves can lead to their dysfunction. Additionally, a family history of varicose veins increases the likelihood of developing this condition.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Occupations that require you to stand for longer periods or sitting for long, can put additional pressure on the veins, hindering blood flow and higher the risk of varicose veins.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy and menopause can weaken vein walls and valves, making women more susceptible to varicose veins.
Obesity
Excess weight puts added pressure on the veins, impairing their ability to transport blood efficiently and potentially leading to the development of varicose veins.
Family History
If you have a family history of varicose veins, you are more likely to get them as well.
What are the Symptoms of Varicose Veins?
The symptoms of varicose veins include -(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins: Diagnosis and Treatment
Go to source)
- Varicose veins are swollen, they become bigger, blue and twisted
- Appearance of spider veins (telangiectasia)
- Most people feel severe pain and heaviness in the area
- Swelling
- Constant itching
- The skin becomes thin, hard, dry and discolored
- Minor injuries in the affected areas can also cause severe bleeding.
These symptoms worsen with standing or sitting for long periods; sitting down with the legs raised is the only way to relieve these problems.
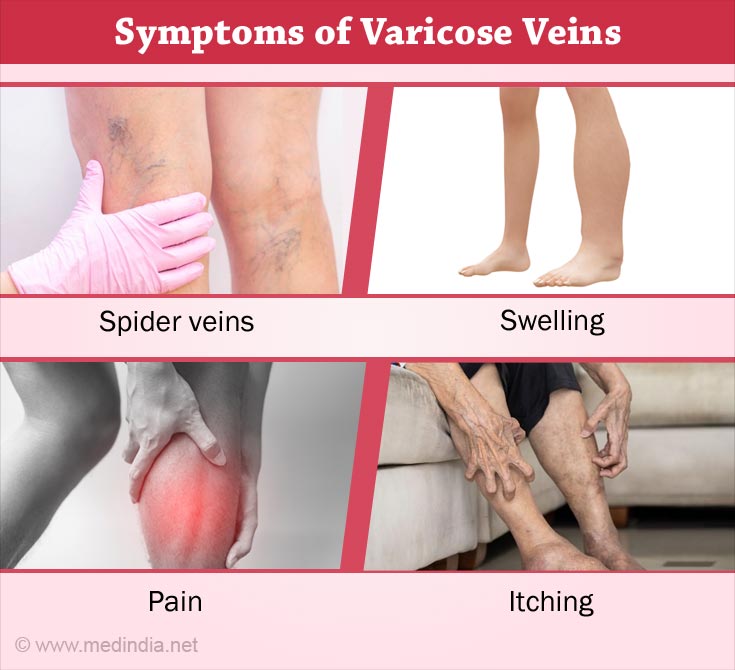
Some people may not experience any symptoms and varicose veins are only a cosmetic problem for them.
How can we Diagnose Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are diagnosed merely by physical examination of the patient while standing or sitting down with dangling legs.
The doctor may recommend the following tests -
- An X-ray of the vein (venogram)(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Three-dimensional CT Venography: A Diagnostic Modality for the Preoperative Assessment of Patients with Varicose Veins
Go to source) - CT venography allows clear visualization of the great and small saphenous veins, perforators and deep veins in the entire lower extremity without interference by arterial images. In addition, this method requires a small amount of contrast medium, which is advantageous for reducing cost and renal damage. Furthermore, it facilitates the selection of effective and efficient strategies when it is used in conjunction with ultrasonography. CT venography may be an optional evaluation method for the treatment of varicose veins.
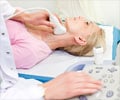
- A duplex ultrasound of the affected leg to tell if there is any problem with the blood flow and to rule out other causes like blood clots. Doppler ultrasound is noninvasive and provides morphological and hemodynamic information, but it takes time for scanning the entire leg, and the accuracy and quality of assessment depends on the skill of the examiner.
When is Procedure for Varicose Vein required?
Treatment for varicose veins is typically recommended when the symptoms and complications associated with them become bothersome or when they significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Some common indications for varicose vein procedures include:
Pain and Discomfort
When varicose veins cause persistent pain, throbbing, aching, or cramping in the legs, treatment may be advised to alleviate these symptoms.
Swelling and Inflammation
Varicose veins can lead to swelling, inflammation, and a feeling of heaviness in the affected leg. Treatment may be considered to reduce these symptoms.
Skin Changes
Skin discoloration, rashes, dryness, and itchiness around the varicose veins can indicate the need for treatment to prevent further skin complications.
Ulcers and Bleeding
In rare cases, varicose veins can develop ulcers or skin sores, which are often difficult to heal. Additionally, if the veins are prone to bleeding, medical intervention may be required.
How can Varicose Veins be Treated?
Several treatment options are available for varicose veins, depending on the severity and specific needs of the patient. These procedures aim to relieve symptoms, improve appearance, and prevent complications. Here are some commonly used treatments (6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Management of varicose veins
Go to source):
Lifestyle Changes
Simple lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting, and elevating the legs can alleviate symptoms and prevent further progression.
Compression Stockings
Wearing compression stockings provides external pressure that helps improve circulation in blood vessels and reduces discomfort associated with varicose veins.
Endo-venous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
EVLA is a minimally invasive treatment that uses laser energy to heat and seal off the affected vein. It is effective for larger varicose veins can be performed under local anesthesia.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
Similar to EVLA, RFA involves using heat energy to close off the damaged vein. A catheter with a radiofrequency device is inserted into the vein to achieve this.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy
This surgical procedure involves making tiny incisions over the varicose veins and removing them through these small cuts. Ambulatory phlebectomy is suitable for larger varicose veins close to the surface of the skin.
Sclerotherapy
This procedure involves injecting a solution directly into the affected vein, causing it to close and eventually fade away. Sclerotherapy is commonly used for smaller varicose veins and spider veins (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Injection sclerotherapy for varicose veins
Go to source).
Varicose Vein Ligation and Stripping
Stripping or vein removal is used to remove larger varicose veins
How to Relieve and Prevent Varicose Veins?
- Don't cross your legs when sitting.
- Exercise regularly. Walking is a good choice. It improves leg and vein strength(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins
Go to source). - Avoid weight gain.
- Avoid standing for prolonged period of time. If your job or hobby require you to stand, shift your weight from one leg to the other every few minutes.
- Wear elastic support stockings(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins
Go to source). - Don't wear clothing or undergarments that are tight or constrict your waist, groin or legs(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins
Go to source).
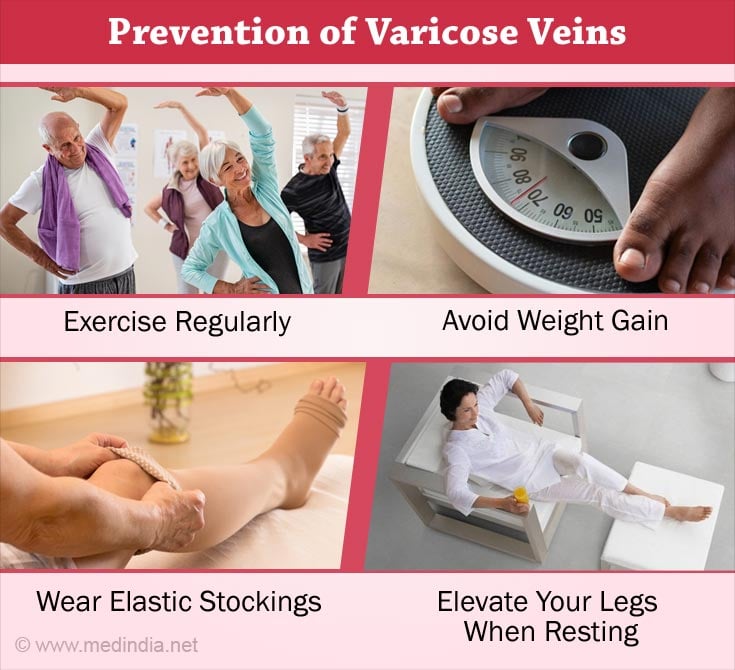
- Eat high-fiber foods like bran cereals, whole grain breads, fresh fruits and vegetables to promote regularity as constipation contributes to varicose veins due to abdominal straining(9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diets for constipation
Go to source). - To prevent swelling, cut your salt intake.
- Exercise your legs. This can be undertaken even if you have a sedentary desk job.
- Elevate your legs when resting(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Varicose Veins
Go to source). - Get up and move about every 35 to 45 minutes when traveling by air or even when sitting in an all day conference. (Opt for an aisle seat in such situations).
- Stop and take short walks at least every 45 minutes when taking long car rides or limited exercise of your legs as advised previously.
- Varicose veins tend to get worse with time. One can ease discomfort and slow varicose veins from getting worse by taking good care of them.