Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis usually responds to home treatment. Taking proper care of skin at home reduces the need for medications.
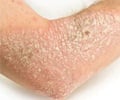
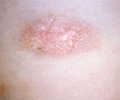
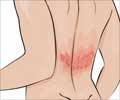
Treatment may vary depending on the appearance (stage) of the lesions. Acute weeping lesions, dry scaly lesions, or chronic dry thickened lesions are treated differently.
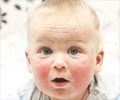
The fingernails of children with infantile eczema should be cut short to prevent them from scratching and aggravating the rash. Infantile eczema usually becomes milder with age and often disappears after age 3 or 4.
Anything that aggravates the symptoms should be avoided. For some patients certain food items, environmental factors like change in weather, usage of wool and lanolin can increase the problem. Temperature changes and stress may cause sweating and changes in the blood vessels of the skin. These aggravate the condition.
Dry skin often makes the condition worse, so bathing and the use of soaps may be reduced. Have short cooler baths and use gentle body washes and cleansers instead of regular soaps. Do not scrub or dry the skin too hard. Apply lubricating creams, lotions or ointment on the skin soon after bathing while the skin is damp. This will help trap moisture in the skin and prevent dryness.
If avoidance of irritants does not reduce symptoms, topical creams and oral medications may be indicated. Topical treatment may include using soothing lotions, topical steroid cream, or other prescribed cream; using mild soaps, or wet dressings. Taking antihistamines can reduce severe itching.
Other treatment options include using immunosuppressant drugs or phototherapy.
Preventive measures:
There is no known preventive measure. The condition tends to run in families. Control of stress and emotional conditions like nervousness, anxiety, depression, etc. can be useful in preventing some cases.