- All You Need To Know About Goiter - (https://www.thyroid.org/goiter/)
- More Information on Goitre - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/goitre/)
- Simple Goiter - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001178.htm)
- Goitre - Causes, Investigation And Management - (https://www.racgp.org.au/afp/2012/august/goitre/)
- Goitre - An Overview - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/goitre)
- Know More About Goitre - (https://www.nhp.gov.in/disease/endocrinal/thyroid-parathyroid/goitre)
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis: A Potential Target of a Chinese Herbal Formula Haizao Yuhu Decoction Acting on Iodine-Deficient Goiter. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27384475)
- Goitre - A Thyroid Swelling - (https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/goitre)
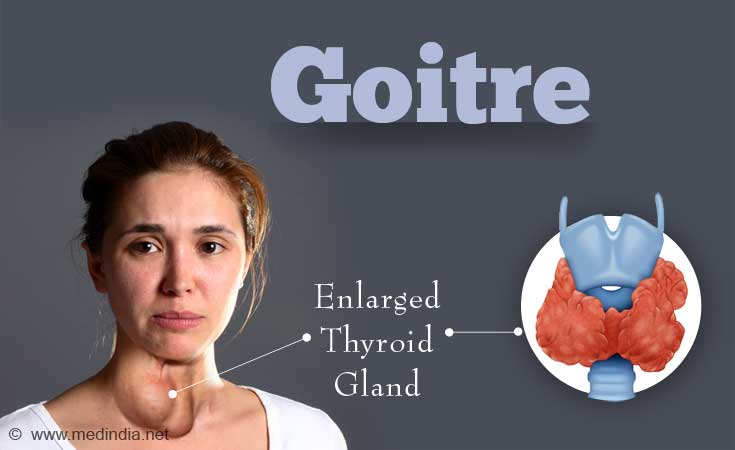
What is Goitre?
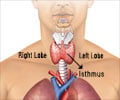
An enlargement of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland which is present at the front of the throat and below the Adam’s apple, is called goitre.
The thyroid gland comprises of two lobes that lie on either side of the windpipe joined by a bridge of tissue called the isthmus. It is controlled by the pituitary gland, which prompts the thyroid to secrete the hormones thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3) by releasing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Excessive stimulation of the thyroid gland by TSH can result in a goitre.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Goitre - An Overview
Go to source)
What are the Types of Goitre?
Goitre is classified as diffuse or nodular.
- In diffuse goitre the whole thyroid gland swells and its smooth to touch
- In nodular goitre, solid or fluid-filled lumps called thyroid nodules develop in the thyroid gland.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Know More About Goitre
Go to source) Nodular goitre is further classified into two types: - Uninodular with only one nodule
- Multinodular with more than one nodule
The nodules may be inactive or toxic
Goitre may also be classified as endemic and sporadic.
- Endemic goitre, occurs due to insufficient dietary iodine intake. More than 10% of the community is usually affected .
- In sporadic goitre, a lesser number of individuals from the community are affected. The risk factors include a positive family history, dietary iodine deficiency, age (over 40 years) and female gender.
What are the Causes of Goitre?
Goitre is the resultant of many factors such as:
- Insufficient iodine in the diet due to inadequate intake of iodine-rich foods or high consumption of certain foods that neutralize iodine, namely cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower. Soy also induces goitre.
- Drugs such as
- lithium and phenylbutazone
- Thyroid cancer such as infiltrating papillary thyroid cancer, lymphoma, and anaplastic thyroid cancer.
- Thyroid nodules
- Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism due to several causes
- Thyroiditis like autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto thyroiditis) and painless (postpartum) thyroiditis. Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
More Information on Goitre
Go to source)
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Goitre?
Symptoms and Signs of goitre include:
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland in the throat. It may appear as a smooth diffuse swelling or with an irregular surface due to the presence of nodules. It moves vertically during swallowing
- Difficulty in swallowing due to a large goitre that presses the esophagus or food pipe
- Difficulty in breathing due to a large goitre that presses the windpipe (trachea)
- Hoarseness of voice

- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism may be present(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Simple Goiter
Go to source)
How do you Diagnose Goitre?
Goitre is diagnosed based on the following:
- Physical examination is performed by a doctor who examines for signs related to thyroid enlargement, such as the size of the gland or nodule, its firmness, mobility and tenderness.
- Blood tests are performed to check for thyroid hormone levels and specific antibodies. The patient is identified to have an underactive thyroid if the TSH is elevated. Some patients with goitre may have normal thyroid hormone levels.
- If the thyroid nodule is larger than 1.0‑1.5 cm in diameter and with TSH level of normal or high, then the patient is advised a fine needle aspiration biopsy. The biopsy may reveal a benign nodule, thyroid cancer, or an uncertain diagnosis. In some cases, an inadequate specimen may be obtained.
- Ultrasound scan or a radioactive iodine scan is performed. A thyroid sonogram or ultrasound sends inaudible sound waves into the neck in such a way that the returning echoes determine the structure of the thyroid and surrounding tissues. A radioactive scan determines if the nodule is a hot nodule (a hyperactive nodule that takes up more radioactive iodine) or a cold nodule (a hypoactive nodule that takes up less radioactive iodine). Cancerous nodules appear as cold nodules on a radioactive thyroid scan, though some benign nodules may also appear cold.(5Goitre - Causes, Investigation And Management
Go to source)

How do you Treat Goitre?
Treatment of goitre depends on the underlying cause:
- Goitre caused due to hyperthyroidism is treated with drugs that slow down the activity of the thyroid gland. Treatment with radioactive iodine destroys some or all of the thyroid’s hormone-producing cells. If these treatments fail to cure the thyroid disease, then the thyroid gland is surgically removed.
- Goitre caused due to hypothyroidism is treated with lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- Goitre due to
iodine deficiency is treated with iodine-rich foods, such as seafood and iodized salt.(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis: A Potential Target of a Chinese Herbal Formula Haizao Yuhu Decoction Acting on Iodine-Deficient Goiter.
Go to source)

- Benign thyroid nodules are reduced in size with the help of medications, destroyed with radioactive iodine treatment or removed using surgical methods.
- Thyroid cancer is removed surgically which is then followed by radioactive iodine treatment.
Thyroidectomy refers to the surgical removal of the thyroid. Thyroidectomy relieves the compression of the nearby structures because of the enlarged gland, thereby improving symptoms relating to difficulty in swallowing, cough or shortness of breath. The different types of thyroidectomy are illustrated below:
- Total thyroidectomy involves the surgical removal of the whole gland.
- Near-total thyroidectomy involves the surgical removal of both the lobes except for a small amount of thyroid tissue.
- Subtotal thyroidectomy leaves 3‑5 g of the tissue on the less affected side of the gland.
A possible after effect of thyroidectomy is recurrent nerve palsy as this nerve could be traumatized during surgery. Complications to the voice, swallowing or both can occur. If the four parathyroid glands which are located close to the thyroid are accidentally removed or injured, the patient's blood calcium levels may drop resulting in tingling, muscle cramps and numbness. A severely low calcium level leads to throat spasm or a seizure.
Endoscopic techniques used to surgically remove the thyroid gland are minimally invasive and the scars are totally invisible. The safety of the operation lies on the quality of the images captured on the endoscopic high-definition camera.(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
All You Need To Know About Goiter
Go to source)
How Do You Prevent Goitre?
Following are some tips to prevent goitre:
- Add only iodized salt to your food
- Eat seafood rich in iodine, such as sea weed, shrimps and shell fish.
- Avoid over exposure to radiation, be it at work place or during any kind of radiation treatment.(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Goitre - A Thyroid Swelling
Go to source)
Health Tips
Here are some common home remedies for treating and preventing goitre.
- Simple exercises, such as neck stretches or other similar exercises for the thyroid gland should be performed on a daily basis. Many fitness freaks suggest aerobic exercises along with jogging for all thyroid problems.
- Food items that can be included to treat goitre include oats, seafood, tomatoes, carrots, lettuce, garlic, strawberries, eggs (yolk), onions, citric fruits, pineapples, bananas, vitamin A rich foods, meat, dairy products, pulses, watermelons, grapes and dates.