About
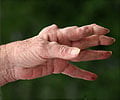
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a chronic health condition characterized by widespread pain and stiffness in the muscles, joints and tendons. It is considered to be a co-morbid disorder.
Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is an enigmatic condition as there is an absence of tissue inflammation. It is referred to as a "syndrome," because it manifests as a combination of signs and symptoms rather than a characteristic clinical entity. The duration of symptoms may vary from months to even years. As a poorly-understood condition, it is a challenge to both the patient and the physician.
FM is often accompanied by tactile
Recent research suggests that fibromyalgia may be gene-controlled, which goes to say that people with fibromyalgia may be genetically predisposed to the health condition. The pain experienced by these patients is genuine and not a fake; this is authenticated by specialists.
Fibromyalgia can occur independently, nevertheless, there is a prevailing theory that FM is a co-morbid diorder; in other words, it occurs alongside another disorder, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus. Most often the original ‘trigger’ gets treated but the fibromyalgia remains. Chronic fatigue syndrome, gluten sensitivity and irritable bowel syndrome are some of the other triggering primary disorders.
Unlike those affected by rheumatic conditions, there is no tissue inflammation in the affected patients, hence there is no accompanying body deformity. There is no internal damage either.
Although fibromyalgia is a common condition that affects muscles, its specific causes remain unknown.
Fibromyalgia predominantly affects women between the age group of 35 years and 55 years, although it can also affect children, men and the elderly. The prevalence of fibromyalgia varies from country to country. In the European countries of Sweden and Britain, fibromyalgia affects 1 percent of the population. In the US, 2 percent of the population has fibromyalgia.
The most commonly recognised types of fibromyalgia are listed below:
- Post traumatic –In this case FM occurs after an accident. The patient initially complains of headaches and thereafter of stiffness of arm/leg and pain.
- Mood related - This type of fibromyalgia occurs if the patient is suffering from anxiety and pain. Mood disorders, such as depression, are common among these patients.
- Hormonal abnormalities - Hyperthyroidism causes increased muscle tension, anxiety and sleep disorder. All these symptoms are also indicative of fibromyalgia.
- Repetitive Traumatic - Repeated injuries may aggravate fibromyalgia symptoms.
No specific tests are available for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia. However there are some tender spots on the body of the patients who have the condition; they should experience pain in at least 11 out of the 18 classic tender points.
Treatment involves a combination of stress reduction, medications, exercise and education.